This Day In History
JFK Jr. killed in plane crash

On July 16, 1999, John F. Kennedy, Jr.; his wife, Carolyn Bessette Kennedy; and her sister, Lauren Bessette, die when the single-engine plane that Kennedy was piloting crashes into the Atlantic Ocean near Martha’s Vineyard, Massachusetts.
John Fitzgerald Kennedy, Jr., was born on November 25, 1960, just a few weeks after his father and namesake was elected the 35th president of the United States. On his third birthday, “John-John” attended the funeral of his assassinated father and was photographed saluting his father’s coffin in a famous and searing image. Along with his sister, Caroline, he was raised in Manhattan by his mother, Jacqueline. After graduating from Brown University and a very brief acting stint, he attended New York University Law School. He passed the bar on his third try and worked in New York as an assistant district attorney, winning all six of his cases. In 1995, he founded the political magazine George, which grew to have a circulation of more than 400,000. Unlike many others in his famous family, he never sought public office himself.
Always in the media spotlight, he was celebrated for the good looks that he inherited from his parents. In 1988, he was named the “Sexiest Man Alive” by People magazine. He was linked romantically with several celebrities, including the actress Daryl Hannah, whom he dated for five years. In September 1996, he married girlfriend Carolyn Bessette, a fashion publicist. The two shared an apartment in New York City, where Kennedy was often seen inline skating in public. Known for his adventurous nature, he nonetheless took pains to separate himself from the more self-destructive behavior of some of the other men in the Kennedy clan.
On July 16, 1999, however, with about 300 hours of flying experience, Kennedy took off from Essex County airport in New Jersey and flew his single-engine plane into a hazy, moonless night. He had turned down an offer by one of his flight instructors to accompany him, saying he “wanted to do it alone.” To reach his destination of Martha’s Vineyard, he would have to fly 200 miles–the final phase over a dark, hazy ocean–and inexperienced pilots can lose sight of the horizon under such conditions. Unable to see shore lights or other landmarks, Kennedy would have to depend on his instruments, but he had not qualified for a license to fly with instruments only. In addition, he was recovering from a broken ankle, which might have affected his ability to pilot his plane.
At Martha’s Vineyard, Kennedy was to drop off his sister-in-law Lauren Bessette, one of his two passengers. From there, Kennedy and his wife, Carolyn, were to fly on to the Kennedy compound on Cape Cod’s Hyannis Port for the marriage of Rory Kennedy, the youngest child of the late Robert F. Kennedy. The Piper Saratoga aircraft never made it to Martha’s Vineyard. Radar data examined later showed the plane plummeting from 2,200 feet to 1,100 feet in a span of 14 seconds, a rate far beyond the aircraft’s safe maximum. It then disappeared from the radar screen.
Kennedy’s plane was reported missing by friends and family members, and an intensive rescue operation was launched by the Coast Guard, the navy, the air force, and civilians. After two days of searching, the thousands of people involved gave up hope of finding survivors and turned their efforts to recovering the wreckage of the aircraft and the bodies. Americans mourned the loss of the “crown prince” of one of the country’s most admired families, a sadness that was especially poignant given the relentless string of tragedies that have haunted the Kennedy family over the years.
On July 21, navy divers recovered the bodies of JFK Jr., his wife, and sister-in-law from the wreckage of the plane, which was lying under 116 feet of water about eight miles off the Vineyard’s shores. The next day, the cremated remains of the three were buried at sea during a ceremony on the USS Briscoe, a navy destroyer. A private mass for JFK Jr. and Carolyn was held on July 23 at the Church of St. Thomas More in Manhattan, where the late Jackie Kennedy Onassis worshipped. President Bill Clinton and his wife, Hillary Rodham Clinton, were among the 300 invited guests. The Kennedy family’s surviving patriarch, Senator Edward M. Kennedy of Massachusetts, delivered a moving eulogy: “From the first day of his life, John seemed to belong not only to our family, but to the American family. He had a legacy, and he learned to treasure it. He was part of a legend, and he learned to live with it.”
Investigators studying the wreckage of the Piper Saratoga found no problems with its mechanical or navigational systems. In their final report released in 2000, the National Transportation Safety Board concluded that the crash was caused by an inexperienced pilot who became disoriented in the dark and lost control.

– History.com Staff
This Day In History
Truman announces development of H-bomb

U.S. President Harry S. Truman publicly announces his decision to support the development of the hydrogen bomb, a weapon theorized to be hundreds of times more powerful than the atomic bombs dropped on Japan during World War II.
Five months earlier, the United States had lost its nuclear supremacy when the Soviet Union successfully detonated an atomic bomb at their test site in Kazakhstan. Then, several weeks after that, British and U.S. intelligence came to the staggering conclusion that German-born Klaus Fuchs, a top-ranking scientist in the U.S. nuclear program, was a spy for the Soviet Union. These two events, and the fact that the Soviets now knew everything that the Americans did about how to build a hydrogen bomb, led Truman to approve massive funding for the superpower race to complete the world’s first “superbomb,” as he described it in his public announcement on January 31.
On November 1, 1952, the United States successfully detonated “Mike,” the world’s first hydrogen bomb, on the Eniwetok Atoll in the Pacific Marshall Islands. The 10.4-megaton thermonuclear device, built upon the Teller-Ulam principles of staged radiation implosion, instantly vaporized an entire island and left behind a crater more than a mile wide. The incredible explosive force of Mike was also apparent from the sheer magnitude of its mushroom cloud–within 90 seconds the mushroom cloud climbed to 57,000 feet and entered the stratosphere. One minute later, it reached 108,000 feet, eventually stabilizing at a ceiling of 120,000 feet. Half an hour after the test, the mushroom stretched 60 miles across, with the base of the head joining the stem at 45,000 feet.
Three years later, on November 22, 1955, the Soviet Union detonated its first hydrogen bomb on the same principle of radiation implosion. Both superpowers were now in possession of the “hell bomb,” as it was known by many Americans, and the world lived under the threat of thermonuclear war for the first time in history.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/truman-announces-development-of-h-bomb
This Day In History
Gandhi assassinated
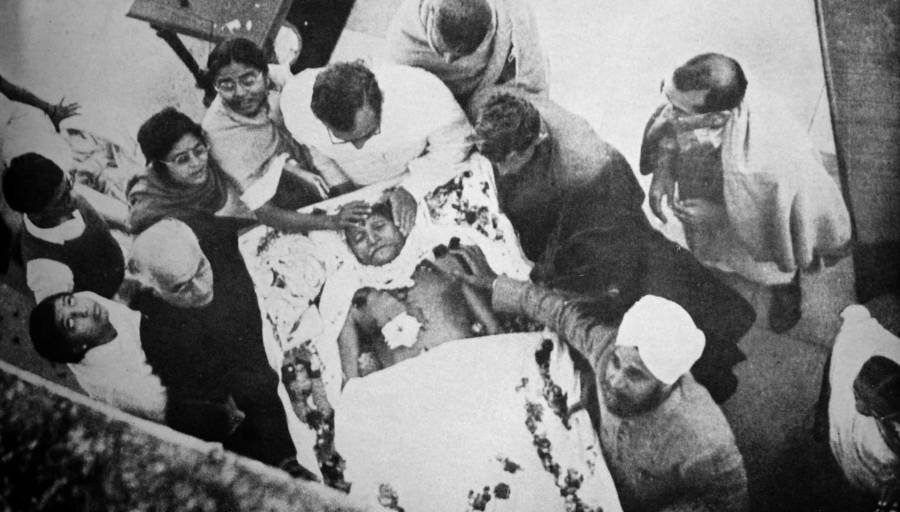

Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, the political and spiritual leader of the Indian independence movement, is assassinated in New Delhi by a Hindu extremist.
Born the son of an Indian official in 1869, Gandhi’s Vaishnava mother was deeply religious and early on exposed her son to Jainism, a morally rigorous Indian religion that advocated nonviolence. Gandhi was an unremarkable student but in 1888 was given an opportunity to study law in England. In 1891, he returned to India, but failing to find regular legal work he accepted in 1893 a one-year contract in South Africa.
Settling in Natal, he was subjected to racism and South African laws that restricted the rights of Indian laborers. Gandhi later recalled one such incident, in which he was removed from a first-class railway compartment and thrown off a train, as his moment of truth. From thereon, he decided to fight injustice and defend his rights as an Indian and a man. When his contract expired, he spontaneously decided to remain in South Africa and launched a campaign against legislation that would deprive Indians of the right to vote. He formed the Natal Indian Congress and drew international attention to the plight of Indians in South Africa. In 1906, the Transvaal government sought to further restrict the rights of Indians, and Gandhi organized his first campaign of satyagraha, or mass civil disobedience. After seven years of protest, he negotiated a compromise agreement with the South African government.
In 1914, Gandhi returned to India and lived a life of abstinence and spirituality on the periphery of Indian politics. He supported Britain in the First World War but in 1919 launched a new satyagraha in protest of Britain’s mandatory military draft of Indians. Hundreds of thousands answered his call to protest, and by 1920 he was leader of the Indian movement for independence. He reorganized the Indian National Congress as a political force and launched a massive boycott of British goods, services, and institutions in India. Then, in 1922, he abruptly called off the satyagraha when violence erupted. One month later, he was arrested by the British authorities for sedition, found guilty, and imprisoned.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/gandhi-assassinated
This Day In History
U.S. Baseball Hall of Fame elects first members
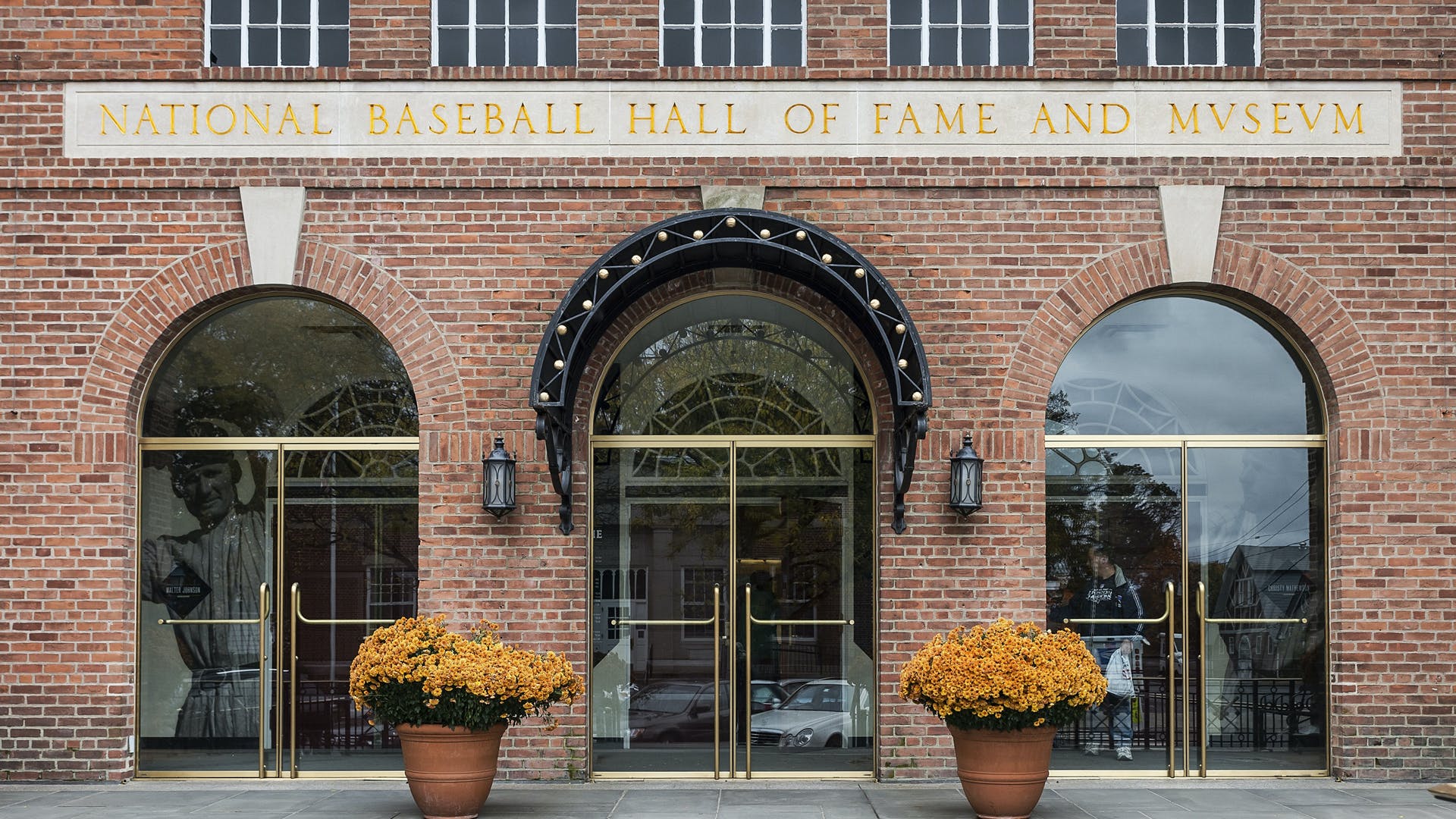

On January 29, 1936, the U.S. Baseball Hall of Fame elects its first members in Cooperstown, New York: Ty Cobb, Babe Ruth, Honus Wagner, Christy Matthewson and Walter Johnson.
The Hall of Fame actually had its beginnings in 1935, when plans were made to build a museum devoted to baseball and its 100-year history. A private organization based in Cooperstown called the Clark Foundation thought that establishing the Baseball Hall of Fame in their city would help to reinvigorate the area’s Depression-ravaged economy by attracting tourists. To help sell the idea, the foundation advanced the idea that U.S. Civil War hero Abner Doubleday invented baseball in Cooperstown. The story proved to be phony, but baseball officials, eager to capitalize on the marketing and publicity potential of a museum to honor the game’s greats, gave their support to the project anyway.
In preparation for the dedication of the Hall of Fame in 1939—thought by many to be the centennial of baseball—the Baseball Writers’ Association of America chose the five greatest superstars of the game as the first class to be inducted: Ty Cobb was the most productive hitter in history; Babe Ruth was both an ace pitcher and the greatest home-run hitter to play the game; Honus Wagner was a versatile star shortstop and batting champion; Christy Matthewson had more wins than any pitcher in National League history; and Walter Johnson was considered one of the most powerful pitchers to ever have taken the mound.
Today, with approximately 350,000 visitors per year, the Hall of Fame continues to be the hub of all things baseball.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/u-s-baseball-hall-of-fame-elects-first-members
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year ago2 hurt, 1 jailed after shooting incident north of Nocona
-

 NEWS5 months ago
NEWS5 months agoSuspect indicted, jailed in Tia Hutson murder
-

 NEWS12 months ago
NEWS12 months agoSO investigating possible murder/suicide
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoWreck takes the life of BHS teen, 16
-
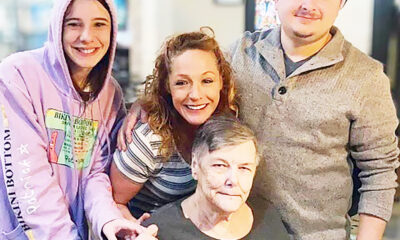
 NEWS9 months ago
NEWS9 months agoMurder unsolved – 1 year later Tia Hutson’s family angry, frustrated with no arrest
-

 NEWS12 months ago
NEWS12 months agoSheriff’s office called out to infant’s death
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoBowie Police face three-hour standoff after possible domestic fight
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoDriver stopped by a man running into the street, robbed at knifepoint





