This Day In History
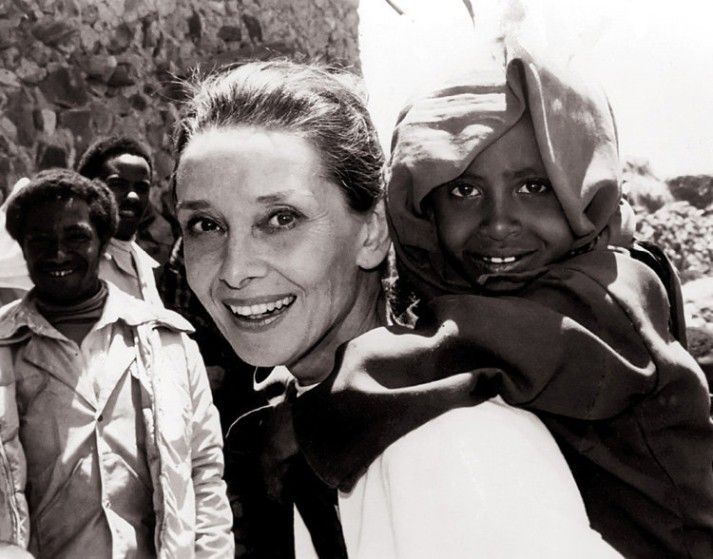
Actress Audrey Hepburn dies

The daughter of an aristocratic Dutch mother and an English businessman father, Hepburn was born in Brussels, Belgium, and educated mostly in England. During World War II, the young Audrey and her mother were in the Netherlands when the Nazis invaded that country. The war left a permanent mark on Hepburn’s family: An uncle and a cousin were executed, and one of her brothers was interned in a Nazi labor camp. At war’s end, Hepburn was finally able to return to England, where she modeled and began landing parts in movies as a chorus girl and dancer. While shooting one of these films in Monaco, the lithe and graceful Hepburn was spotted by the French author Colette, who recommended her for the starring role in the upcoming theatrical adaptation of her novel Gigi.
Gigi opened in November 1951 at New York City’s Fulton Theater, and Hepburn received glowing reviews for her performance. Impressed with her screen test, the director William Wyler held production on his film Roman Holiday while Hepburn finished her run on Broadway. “That girl,” Wyler is said to have remarked after filming was completed, “is going to be the biggest star in Hollywood.” After the release of Roman Holiday in 1953, his prediction seemed well on its way to coming true: Hepburn won an Academy Award for Best Actress for her role as a princess on the loose in Rome who falls in love with a journalist (Gregory Peck). The same year, she won a Tony Award for her starring turn in Broadway’s Ondine.
Slim, elegant and unfailingly stylish, Hepburn turned the image of the bosomy blonde Hollywood starlet on its head, presenting a new ideal of beauty for millions of moviegoers. In Sabrina (1954), Funny Face (1957) and Love in the Afternoon (1957), she matched off with Hollywood’s leading men (William Holden and Humphrey Bogart, Fred Astaire, and Gary Cooper, respectively). Hepburn’s embodiment of Holly Golightly, the ultimate free spirit, in Breakfast at Tiffany’s (1961) was one of her most enduringly popular roles, and earned her a fourth Oscar nomination for Best Actress. (She was also nominated for Sabrina and 1959’s A Nun’s Story). In 1964, controversy flared when Hepburn was chosen to play Eliza Doolittle in the film version of the musical My Fair Lady, beating out Julie Andrews, who had originated the role on Broadway. Playing opposite Rex Harrison, Hepburn acquitted herself well, although her singing was dubbed (by Marni Nixon).
In 1967, Hepburn got her fifth Academy Award nomination for her performance as a blind woman whose house is burglarized in Wait Until Dark. Soon after that, she left full-time acting and lived mostly in Switzerland, appearing infrequently in movies that were both praised (1976’s Robin and Marian with Sean Connery) and panned (1979’s Bloodline and 1981’s They All Laughed). Married to the actor Mel Ferrer in 1954, Hepburn had two sons with him before they divorced in 1968; the following year she married Andrea Dotti, an Italian psychiatrist, with whom she had one son. They later divorced, and she began a relationship with Robert Wolders, a Dutch actor, in 1980.
Hepburn’s most significant work over the last two decades of her life was not captured on film. Named a special ambassador for UNICEF, the United Nation’s children’s fund, in 1988, Hepburn traveled extensively raising money and awareness for the organization. Her UNICEF field trips spanned the globe, from Guatemala, Honduras, Venezuela and El Salvador, to Turkey, Thailand, Bangladesh and Sudan. In addition to field work, Hepburn was an eloquent public voice for the organization, testifying before the U.S. Congress, participating in the World Summit for Children and giving numerous speeches and interviews about UNICEF’s work. In 1992, she was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom.
Even after she was diagnosed with cancer, Hepburn continued her travel and work for UNICEF. Mourned by countless fans, she was posthumously given the Jean Hersholt Humanitarian Award at the 1993 Academy Awards, which her son accepted on her behalf. In her last screen appearance–Steven Spielberg’s Always (1989)–Hepburn played an angel guiding the movie’s protagonist to heaven, and the role served as a fitting reflection of the screen goddess’s public image during the last years of her life.
– History.com Staff
This Day In History
Truman announces development of H-bomb

U.S. President Harry S. Truman publicly announces his decision to support the development of the hydrogen bomb, a weapon theorized to be hundreds of times more powerful than the atomic bombs dropped on Japan during World War II.
Five months earlier, the United States had lost its nuclear supremacy when the Soviet Union successfully detonated an atomic bomb at their test site in Kazakhstan. Then, several weeks after that, British and U.S. intelligence came to the staggering conclusion that German-born Klaus Fuchs, a top-ranking scientist in the U.S. nuclear program, was a spy for the Soviet Union. These two events, and the fact that the Soviets now knew everything that the Americans did about how to build a hydrogen bomb, led Truman to approve massive funding for the superpower race to complete the world’s first “superbomb,” as he described it in his public announcement on January 31.
On November 1, 1952, the United States successfully detonated “Mike,” the world’s first hydrogen bomb, on the Eniwetok Atoll in the Pacific Marshall Islands. The 10.4-megaton thermonuclear device, built upon the Teller-Ulam principles of staged radiation implosion, instantly vaporized an entire island and left behind a crater more than a mile wide. The incredible explosive force of Mike was also apparent from the sheer magnitude of its mushroom cloud–within 90 seconds the mushroom cloud climbed to 57,000 feet and entered the stratosphere. One minute later, it reached 108,000 feet, eventually stabilizing at a ceiling of 120,000 feet. Half an hour after the test, the mushroom stretched 60 miles across, with the base of the head joining the stem at 45,000 feet.
Three years later, on November 22, 1955, the Soviet Union detonated its first hydrogen bomb on the same principle of radiation implosion. Both superpowers were now in possession of the “hell bomb,” as it was known by many Americans, and the world lived under the threat of thermonuclear war for the first time in history.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/truman-announces-development-of-h-bomb
This Day In History
Gandhi assassinated
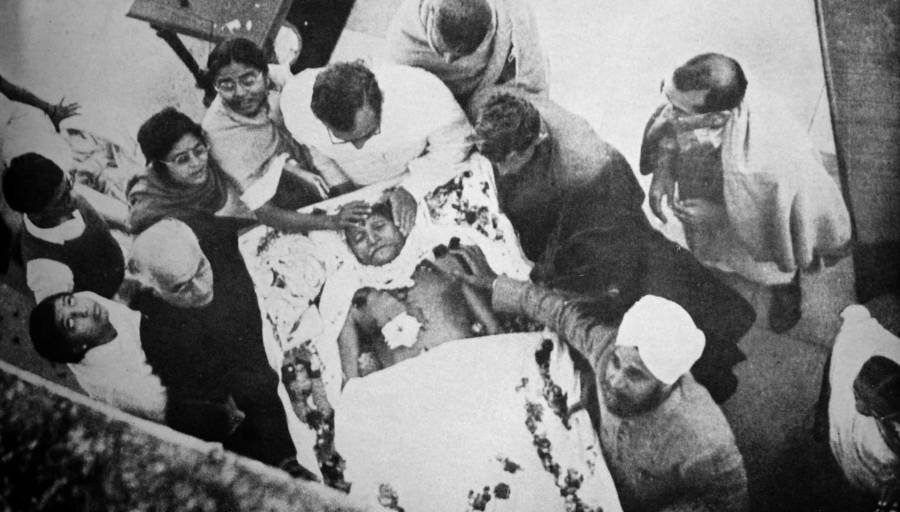

Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, the political and spiritual leader of the Indian independence movement, is assassinated in New Delhi by a Hindu extremist.
Born the son of an Indian official in 1869, Gandhi’s Vaishnava mother was deeply religious and early on exposed her son to Jainism, a morally rigorous Indian religion that advocated nonviolence. Gandhi was an unremarkable student but in 1888 was given an opportunity to study law in England. In 1891, he returned to India, but failing to find regular legal work he accepted in 1893 a one-year contract in South Africa.
Settling in Natal, he was subjected to racism and South African laws that restricted the rights of Indian laborers. Gandhi later recalled one such incident, in which he was removed from a first-class railway compartment and thrown off a train, as his moment of truth. From thereon, he decided to fight injustice and defend his rights as an Indian and a man. When his contract expired, he spontaneously decided to remain in South Africa and launched a campaign against legislation that would deprive Indians of the right to vote. He formed the Natal Indian Congress and drew international attention to the plight of Indians in South Africa. In 1906, the Transvaal government sought to further restrict the rights of Indians, and Gandhi organized his first campaign of satyagraha, or mass civil disobedience. After seven years of protest, he negotiated a compromise agreement with the South African government.
In 1914, Gandhi returned to India and lived a life of abstinence and spirituality on the periphery of Indian politics. He supported Britain in the First World War but in 1919 launched a new satyagraha in protest of Britain’s mandatory military draft of Indians. Hundreds of thousands answered his call to protest, and by 1920 he was leader of the Indian movement for independence. He reorganized the Indian National Congress as a political force and launched a massive boycott of British goods, services, and institutions in India. Then, in 1922, he abruptly called off the satyagraha when violence erupted. One month later, he was arrested by the British authorities for sedition, found guilty, and imprisoned.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/gandhi-assassinated
This Day In History
U.S. Baseball Hall of Fame elects first members

On January 29, 1936, the U.S. Baseball Hall of Fame elects its first members in Cooperstown, New York: Ty Cobb, Babe Ruth, Honus Wagner, Christy Matthewson and Walter Johnson.
The Hall of Fame actually had its beginnings in 1935, when plans were made to build a museum devoted to baseball and its 100-year history. A private organization based in Cooperstown called the Clark Foundation thought that establishing the Baseball Hall of Fame in their city would help to reinvigorate the area’s Depression-ravaged economy by attracting tourists. To help sell the idea, the foundation advanced the idea that U.S. Civil War hero Abner Doubleday invented baseball in Cooperstown. The story proved to be phony, but baseball officials, eager to capitalize on the marketing and publicity potential of a museum to honor the game’s greats, gave their support to the project anyway.
In preparation for the dedication of the Hall of Fame in 1939—thought by many to be the centennial of baseball—the Baseball Writers’ Association of America chose the five greatest superstars of the game as the first class to be inducted: Ty Cobb was the most productive hitter in history; Babe Ruth was both an ace pitcher and the greatest home-run hitter to play the game; Honus Wagner was a versatile star shortstop and batting champion; Christy Matthewson had more wins than any pitcher in National League history; and Walter Johnson was considered one of the most powerful pitchers to ever have taken the mound.
Today, with approximately 350,000 visitors per year, the Hall of Fame continues to be the hub of all things baseball.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/u-s-baseball-hall-of-fame-elects-first-members
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year ago2 hurt, 1 jailed after shooting incident north of Nocona
-

 NEWS5 months ago
NEWS5 months agoSuspect indicted, jailed in Tia Hutson murder
-

 NEWS12 months ago
NEWS12 months agoSO investigating possible murder/suicide
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoWreck takes the life of BHS teen, 16
-
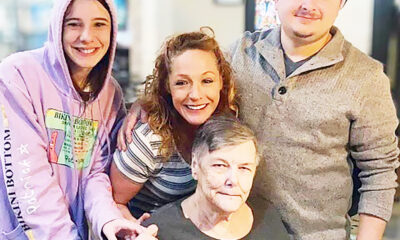
 NEWS9 months ago
NEWS9 months agoMurder unsolved – 1 year later Tia Hutson’s family angry, frustrated with no arrest
-

 NEWS12 months ago
NEWS12 months agoSheriff’s office called out to infant’s death
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoBowie Police face three-hour standoff after possible domestic fight
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoDriver stopped by a man running into the street, robbed at knifepoint








