This Day In History
1929 Valentine’s Day Massacre takes place

In Chicago, gunmen in the suspected employment of organized-crime boss Al Capone murder seven members of the George “Bugs” Moran North Siders gang in a garage on North Clark Street. The so-called St. Valentine’s Day Massacre stirred a media storm centered on Capone and his illegal Prohibition-era activities and motivated federal authorities to redouble their efforts to find evidence incriminating enough to take him off the streets.
Alphonse Capone was born in Brooklyn in 1899, the son of Italian immigrants from Naples. The fourth of nine children, he quit school after the sixth grade and joined a street gang. He became acquainted with Johnny Torrio, a crime boss who operated in Chicago and New York, and at the age of 18 Capone was employed at a Coney Island club owned by gangster Frankie Yale. It was while working there that his face was slashed in a brawl, earning him the nickname “Scarface.”
In 1917, his girlfriend became pregnant and they married, and the couple moved with their son to Baltimore, where Capone attempted a respectable life working as a bookkeeper. In 1921, however, his old friend Johnny Torrio lured him to Chicago, where Torrio had built up an impressive crime syndicate and was beginning to make a fortune on the illicit commerce of alcohol, which was banned in 1919 by the 18th Amendment to the Constitution.
Capone demonstrated considerable business acumen and was appointed manager of a Torrio speakeasy. Later, Torrio put him charge of the suburb of Cicero. Unlike his boss, who was always discreet, Capone achieved notoriety as he fought for control of Cicero and was even tried (unsuccessfully) for murder.
In 1925, Torrio was shot four times by Bugs Moran and Hymie Weiss, who were associates of a gangster slain by Torrio’s men. Torrio lived, but four weeks later he appeared in court and was sentenced to nine months stemming from a police raid of a brewery he owned. About a month later, he called Capone from jail to tell him that he was retiring and handing the business over to him.
Capone moved his headquarters to the luxurious Metropole Hotel, where he became a visible figure in Chicago public life as his crime empire steadily expanded. After a prosecutor was killed by some of Capone’s henchmen, the Chicago police moved aggressively against his criminal operations, but they couldn’t make any charges stick. Capone bought a luxurious estate in Miami as a retreat from all this unwanted attention.
Capone was in Florida in February 1929 when he gave the go-ahead for the assassination of Bugs Moran. On February 13, a bootlegger called Moran and offered to sell him a truckload of high quality whiskey at a low price. Moran took the bait and the next morning pulled up to the delivery location where he was to meet several associates and purchase the whisky. He was running a little late, and just as he was pulling up to the garage he saw what looked like two policemen and two detectives get out of an unmarked car and head to the door. Thinking he had nearly avoided being caught in a police raid, Moran drove off. The four men, however, were Capone’s assassins, and they were only entering the building before Moran’s arrival because they had mistaken one of the seven men inside for the boss himself.
Wearing their stolen police uniforms and heavily armed, Capone’s henchmen surprised Moran’s men, who agreed to line up against the wall. Thinking they had fallen prey to a routine police raid, they allowed themselves to be disarmed. A moment later, they were gunned down in a hail of shotgun and submachine-gun fire. Six were killed instantly, and the seventh survived for less than an hour.
Americans were shocked and outraged by the cold-blooded Valentine’s Day killings, and many questioned whether the sin of intemperance outweighed the evil of Prohibition-era gangsters like Capone. Although, as usual, he had an air-tight alibi, few doubted his role in the massacre. The authorities, particularly affronted by the hit men’s use of police uniforms, vowed to bring him to justice.
With a mandate from Herbert Hoover, the new president, the Treasury Department led the assault against Capone, hoping to uncover enough evidence of Prohibition offenses and federal income tax evasion to bring him to justice. In May 1929, Capone was convicted for carrying a concealed weapon and sent to prison for 10 months. Meanwhile, Treasury agents, like Eliot Ness, continued to gather evidence.
In June 1931, Capone was indicted for income tax evasion. On October 17, primarily on the basis of testimony by two former bookkeepers, he was found guilty on several counts. One week later, he was sentenced to 11 years in prison and $80,000 in fines and court costs. He entered Atlanta penitentiary in 1932 and in 1934 was transferred to the new Alcatraz Island prison in San Francisco Bay. By that time, Prohibition had been repealed, and Capone’s empire had collapsed.
At Alcatraz, the syphilis Capone had contracted in his youth entered a late stage, and he spent his last year in prison in the hospital ward. In 1939, he was released after only six and a half years in jail as the result of good behavior and work credits. He was treated in a Baltimore hospital and in 1940 retired to his Miami estate, where he lived until his death in 1947. He was outlived by his rival Bugs Moran, who later died of lung cancer while serving a 10-year sentence in Kansas for bank robbery.
Source: www.history.com
This Day In History
Truman announces development of H-bomb

U.S. President Harry S. Truman publicly announces his decision to support the development of the hydrogen bomb, a weapon theorized to be hundreds of times more powerful than the atomic bombs dropped on Japan during World War II.
Five months earlier, the United States had lost its nuclear supremacy when the Soviet Union successfully detonated an atomic bomb at their test site in Kazakhstan. Then, several weeks after that, British and U.S. intelligence came to the staggering conclusion that German-born Klaus Fuchs, a top-ranking scientist in the U.S. nuclear program, was a spy for the Soviet Union. These two events, and the fact that the Soviets now knew everything that the Americans did about how to build a hydrogen bomb, led Truman to approve massive funding for the superpower race to complete the world’s first “superbomb,” as he described it in his public announcement on January 31.
On November 1, 1952, the United States successfully detonated “Mike,” the world’s first hydrogen bomb, on the Eniwetok Atoll in the Pacific Marshall Islands. The 10.4-megaton thermonuclear device, built upon the Teller-Ulam principles of staged radiation implosion, instantly vaporized an entire island and left behind a crater more than a mile wide. The incredible explosive force of Mike was also apparent from the sheer magnitude of its mushroom cloud–within 90 seconds the mushroom cloud climbed to 57,000 feet and entered the stratosphere. One minute later, it reached 108,000 feet, eventually stabilizing at a ceiling of 120,000 feet. Half an hour after the test, the mushroom stretched 60 miles across, with the base of the head joining the stem at 45,000 feet.
Three years later, on November 22, 1955, the Soviet Union detonated its first hydrogen bomb on the same principle of radiation implosion. Both superpowers were now in possession of the “hell bomb,” as it was known by many Americans, and the world lived under the threat of thermonuclear war for the first time in history.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/truman-announces-development-of-h-bomb
This Day In History
Gandhi assassinated
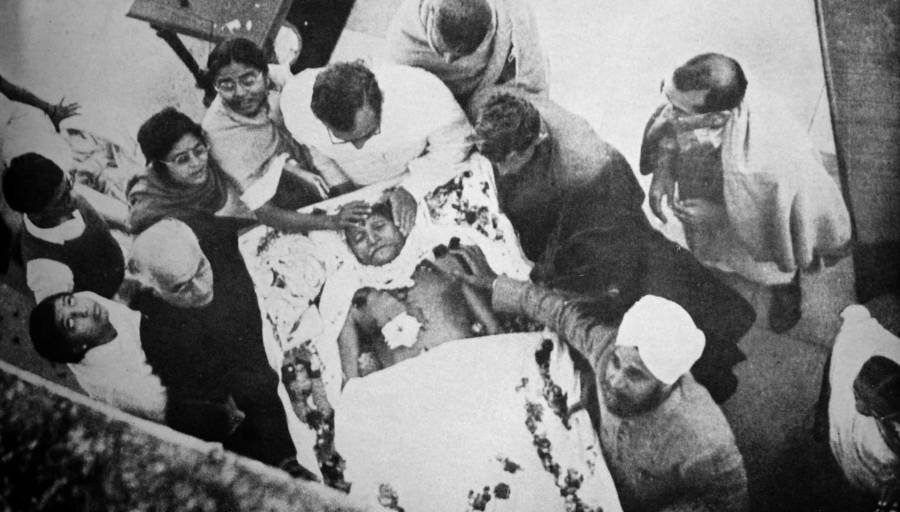

Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, the political and spiritual leader of the Indian independence movement, is assassinated in New Delhi by a Hindu extremist.
Born the son of an Indian official in 1869, Gandhi’s Vaishnava mother was deeply religious and early on exposed her son to Jainism, a morally rigorous Indian religion that advocated nonviolence. Gandhi was an unremarkable student but in 1888 was given an opportunity to study law in England. In 1891, he returned to India, but failing to find regular legal work he accepted in 1893 a one-year contract in South Africa.
Settling in Natal, he was subjected to racism and South African laws that restricted the rights of Indian laborers. Gandhi later recalled one such incident, in which he was removed from a first-class railway compartment and thrown off a train, as his moment of truth. From thereon, he decided to fight injustice and defend his rights as an Indian and a man. When his contract expired, he spontaneously decided to remain in South Africa and launched a campaign against legislation that would deprive Indians of the right to vote. He formed the Natal Indian Congress and drew international attention to the plight of Indians in South Africa. In 1906, the Transvaal government sought to further restrict the rights of Indians, and Gandhi organized his first campaign of satyagraha, or mass civil disobedience. After seven years of protest, he negotiated a compromise agreement with the South African government.
In 1914, Gandhi returned to India and lived a life of abstinence and spirituality on the periphery of Indian politics. He supported Britain in the First World War but in 1919 launched a new satyagraha in protest of Britain’s mandatory military draft of Indians. Hundreds of thousands answered his call to protest, and by 1920 he was leader of the Indian movement for independence. He reorganized the Indian National Congress as a political force and launched a massive boycott of British goods, services, and institutions in India. Then, in 1922, he abruptly called off the satyagraha when violence erupted. One month later, he was arrested by the British authorities for sedition, found guilty, and imprisoned.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/gandhi-assassinated
This Day In History
U.S. Baseball Hall of Fame elects first members

On January 29, 1936, the U.S. Baseball Hall of Fame elects its first members in Cooperstown, New York: Ty Cobb, Babe Ruth, Honus Wagner, Christy Matthewson and Walter Johnson.
The Hall of Fame actually had its beginnings in 1935, when plans were made to build a museum devoted to baseball and its 100-year history. A private organization based in Cooperstown called the Clark Foundation thought that establishing the Baseball Hall of Fame in their city would help to reinvigorate the area’s Depression-ravaged economy by attracting tourists. To help sell the idea, the foundation advanced the idea that U.S. Civil War hero Abner Doubleday invented baseball in Cooperstown. The story proved to be phony, but baseball officials, eager to capitalize on the marketing and publicity potential of a museum to honor the game’s greats, gave their support to the project anyway.
In preparation for the dedication of the Hall of Fame in 1939—thought by many to be the centennial of baseball—the Baseball Writers’ Association of America chose the five greatest superstars of the game as the first class to be inducted: Ty Cobb was the most productive hitter in history; Babe Ruth was both an ace pitcher and the greatest home-run hitter to play the game; Honus Wagner was a versatile star shortstop and batting champion; Christy Matthewson had more wins than any pitcher in National League history; and Walter Johnson was considered one of the most powerful pitchers to ever have taken the mound.
Today, with approximately 350,000 visitors per year, the Hall of Fame continues to be the hub of all things baseball.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/u-s-baseball-hall-of-fame-elects-first-members
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year ago2 hurt, 1 jailed after shooting incident north of Nocona
-

 NEWS5 months ago
NEWS5 months agoSuspect indicted, jailed in Tia Hutson murder
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoSO investigating possible murder/suicide
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoWreck takes the life of BHS teen, 16
-
 NEWS9 months ago
NEWS9 months agoMurder unsolved – 1 year later Tia Hutson’s family angry, frustrated with no arrest
-

 NEWS12 months ago
NEWS12 months agoSheriff’s office called out to infant’s death
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoBowie Police face three-hour standoff after possible domestic fight
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoDriver stopped by a man running into the street, robbed at knifepoint





