COUNTY LIFE
History Channel points to 8 things you may not know about Daylight Saving Time

1. It’s “daylight saving time,” not “daylight savings time.”
Many people render the term’s second word in its plural form. However,
since the word “saving” acts as part of an adjective rather than a verb,
the singular is grammatically correct.
2. Though in favor of maximizing daylight waking hours, Benjamin Franklin did not originate the idea of moving clocks forward.
By the time he was a 78-year-old American envoy in Paris in 1784, the man who espoused the virtues of “early to bed and early to rise” was not practicing what he preached. After being unpleasantly stirred from sleep at 6 a.m. by the summer sun, the founding father penned a satirical essay in which he calculated that Parisians, simply by waking up at dawn, could save the modern-day equivalent of $200 million through “the economy of using sunshine instead of candles.” As a result of this essay, Franklin is often erroneously given the honor of “inventing” daylight saving time, but he only proposed a change in sleep schedules—not the time itself.
3. Englishman William Willett led the first campaign to implement daylight saving time.
While on an early-morning horseback ride around the desolate outskirts of London in 1905, Willett had an epiphany that the United Kingdom should move its clocks forward by 80 minutes between April and October so that more people could enjoy the plentiful sunlight. The Englishman published the 1907 brochure “The Waste of Daylight” and spent much of his personal fortune evangelizing with missionary zeal for the adoption of “summertime.” Year after year, however, the British Parliament stymied the measure, and Willett died in 1915 at age 58 without ever seeing his idea come to fruition.
4. Germany was the first country to enact daylight saving time.
It took World War I for Willett’s dream to come true, but on April 30,
1916, Germany embraced daylight saving time to conserve electricity. (He
may have been horrified to learn that Britain’s wartime enemy followed
his recommendations before his homeland.) Weeks later, the United
Kingdom followed suit and introduced “summer time.”
5. Daylight saving time in the United States was not intended to benefit farmers, as many people think.
Contrary to popular belief, American farmers did not lobby for daylight
saving to have more time to work in the fields; in fact, the agriculture
industry was deeply opposed to the time switch when it was first
implemented on March 31, 1918, as a wartime measure. The sun, not the
clock, dictated farmers’ schedules, so daylight saving was very
disruptive. Farmers had to wait an extra hour for dew to evaporate to
harvest hay, hired hands worked less since they still left at the same
time for dinner and cows weren’t ready to be milked an hour earlier to
meet shipping schedules. Agrarian interests led the fight for the 1919
repeal of national daylight saving time, which passed after Congress
voted to override President Woodrow Wilson’s veto. Rather than rural
interests, it has been urban entities such as retail outlets and
recreational businesses that have championed daylight saving over the
decades.
6. For decades, daylight saving in the United States was a confounding patchwork of local practices.
After the national repeal in 1919, some states and cities, including New
York City and Chicago, continued to shift their clocks. National
daylight saving time returned during World War II, but after its repeal
three weeks after war’s end the confusing hodgepodge resumed. States and
localities could start and end daylight saving whenever they pleased, a
system that Time magazine (an aptly named source) described in 1963 as
“a chaos of clocks.” In 1965 there were 23 different pairs of start and
end dates in Iowa alone, and St. Paul, Minnesota, even began daylight
saving two weeks before its twin city, Minneapolis. Passengers on a
35-mile bus ride from Steubenville, Ohio, to Moundsville, West Virginia,
passed through seven time changes. Order finally came in 1966 with the
enactment of the Uniform Time Act, which standardized daylight saving
time from the last Sunday in April to the last Sunday in October,
although states had the option of remaining on standard time year-round.
7. Not everyone in the United States springs forward and falls back.
Hawaii and Arizona—with the exception of the state’s Navajo Nation—do
not observe daylight saving time, and the U.S. territories of American
Samoa, Guam, Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands and the Northern Mariana
Islands also remain on standard time year-round. Some Amish communities
also choose not to participate in daylight saving time. (Around the
world, only about one-quarter of the world’s population, in
approximately 70 countries, observe daylight saving. Since their
daylight hours don’t vary much from season to season, countries closer
to the equator have little need to deviate from standard time.)
8. Evidence does not conclusively point to energy conservation as a result of daylight saving.
Dating back to Willett, daylight saving advocates have touted energy
conservation as an economic benefit. A U.S. Department of Transportation
study in the 1970s concluded that total electricity savings associated
with daylight saving time amounted to about 1 percent in the spring and
fall months. As air conditioning has become more widespread, however,
more recent studies have found that cost savings on lighting are more
than offset by greater cooling expenses. University of California Santa
Barbara economists calculated that Indiana’s move to statewide daylight
saving time in 2006 led to a 1-percent rise in residential electricity
use through additional demand for air conditioning on summer evenings
and heating in early spring and late fall mornings. Some also argue that
increased recreational activity during daylight saving results in
greater gasoline consumption.
COUNTY LIFE
Cruisin’ Nocona kicks off on Friday

From a road trip around North Texas to a colorful car show, Nocona is gearing up for its 11th annual springtime festival Cruisin’ Nocona on May 3-4 with lots of family fun activities.
Enjoy the popular Poker Cruise on May 3 as drivers travel a 120-mile trek through the countryside of Montague County enjoying several stops along the way before looping back to Nocona for lunch.
Early-bird registration is $50. Forms are available at the Nocona Chamber of Commerce office at 304 Clay St. #3 or go online to Nocona.org/events to get a form. After April 25 the cost goes up to $65.
There will be on-site registration from 9 – 10:30 a.m. that day at 915 E. U.S. Highway 82, where the cruise starts at 11 a.m. Each driver gets a goodie bag with a Cruisin’ Nocona T-shirt and ticket for the cruise lunch. Additional lunch tickets may be purchased for $20.
First-third place prizes will be awarded to the best poker hands. There will be a big truck light show at 8:30 p.m. at The V at 8:30 p.m. Friday night.
A pancake breakfast served from 8-10 a.m. at The V opens Saturday morning followed by downtown Nocona being filled with classic cars and big trucks for Cruisin’ Car Show. This is the second year to include the big trucks set up along Clay and West Walnut Streets.
Prizes will be awarded to the top 10 cars and pickups, top five motorcycles, Big Truck People’s Choice and Big Truck that traveled the farthest to the show. All makes and models welcomed to enter. Forms are available on the chamber’s website.
The car show will have registration from 10 a.m. to 1 p.m. at Clay and W. Walnut with judging from 1-3 p.m. Awards will be presented at 4 p.m. at the H.J. Justin Building, 100 Clay.
There will be a power wheel car show from 3-4 p.m. in the Justin building. Cecil Allen Moore will entertain at the same location starting at 5 p.m.
COUNTY LIFE
3 Bowie seniors ‘sign’ for their future education
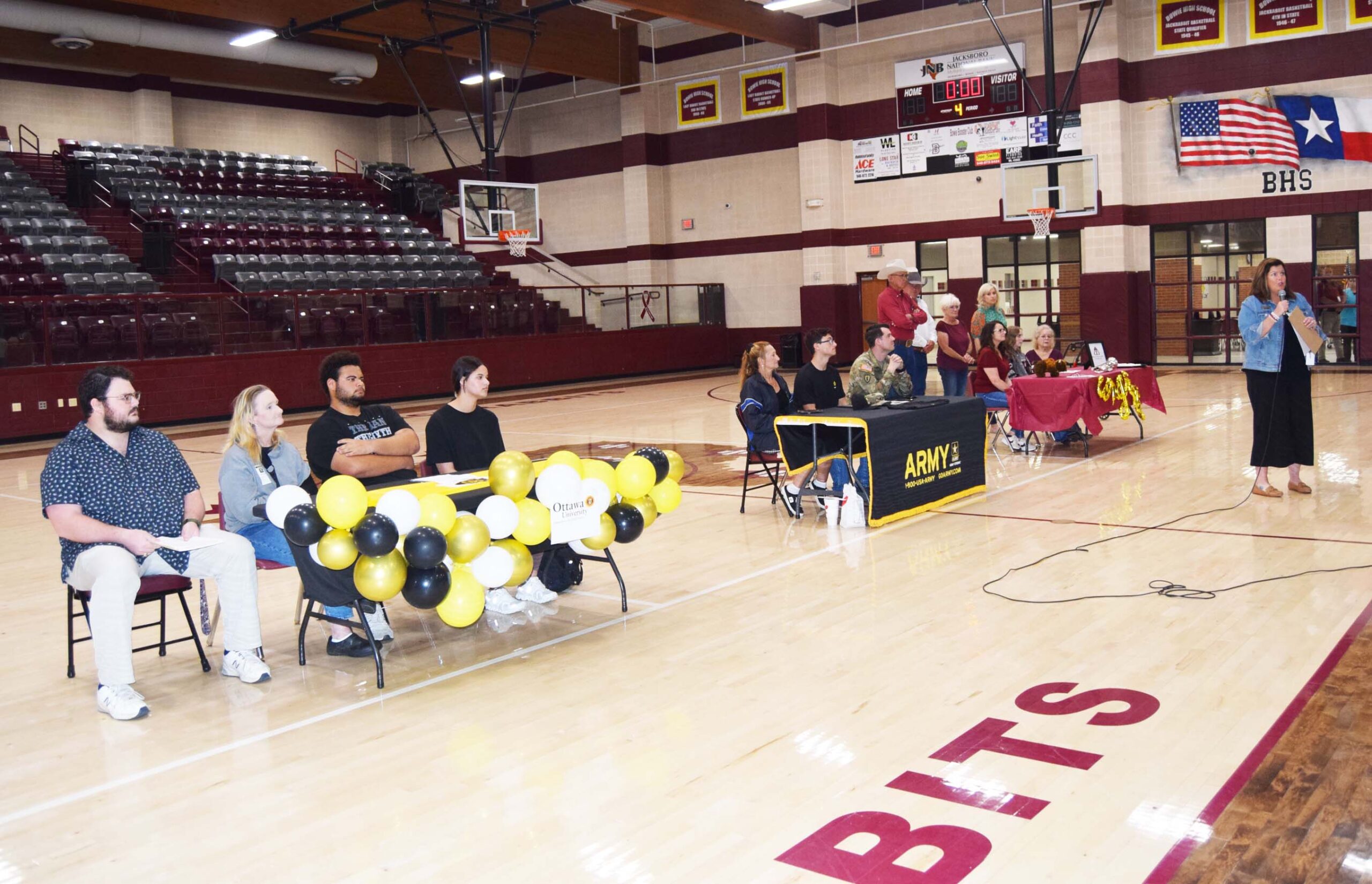

Bowie High School staff and students celebrated its first “Signing Day” on April 25 looking on as three seniors signed their letters of intent to pursue different paths to higher education.
Principal Joanne Keeler said she was excited to present this program and show students the success they can have if they work hard and they also could be signing up for their future. She hopes to see the program expand adding more students who are planning their futures.
Jacobi McGregor signed his letter of intent to attend Ottawa University in Kansas on a powerflifting scholarship. He plans to study sports administration.
Iron Atkinson will be joining the United States Army. His grandmother Sherri Waldrop, looked on as he signed the paperwork.
Traycee Stewart, daughter of Susan and James Stewart, will attending West Texas State A&M University on a music education scholarship.
Read the full story on signing day in the mid-week Bowie News.
COUNTY LIFE
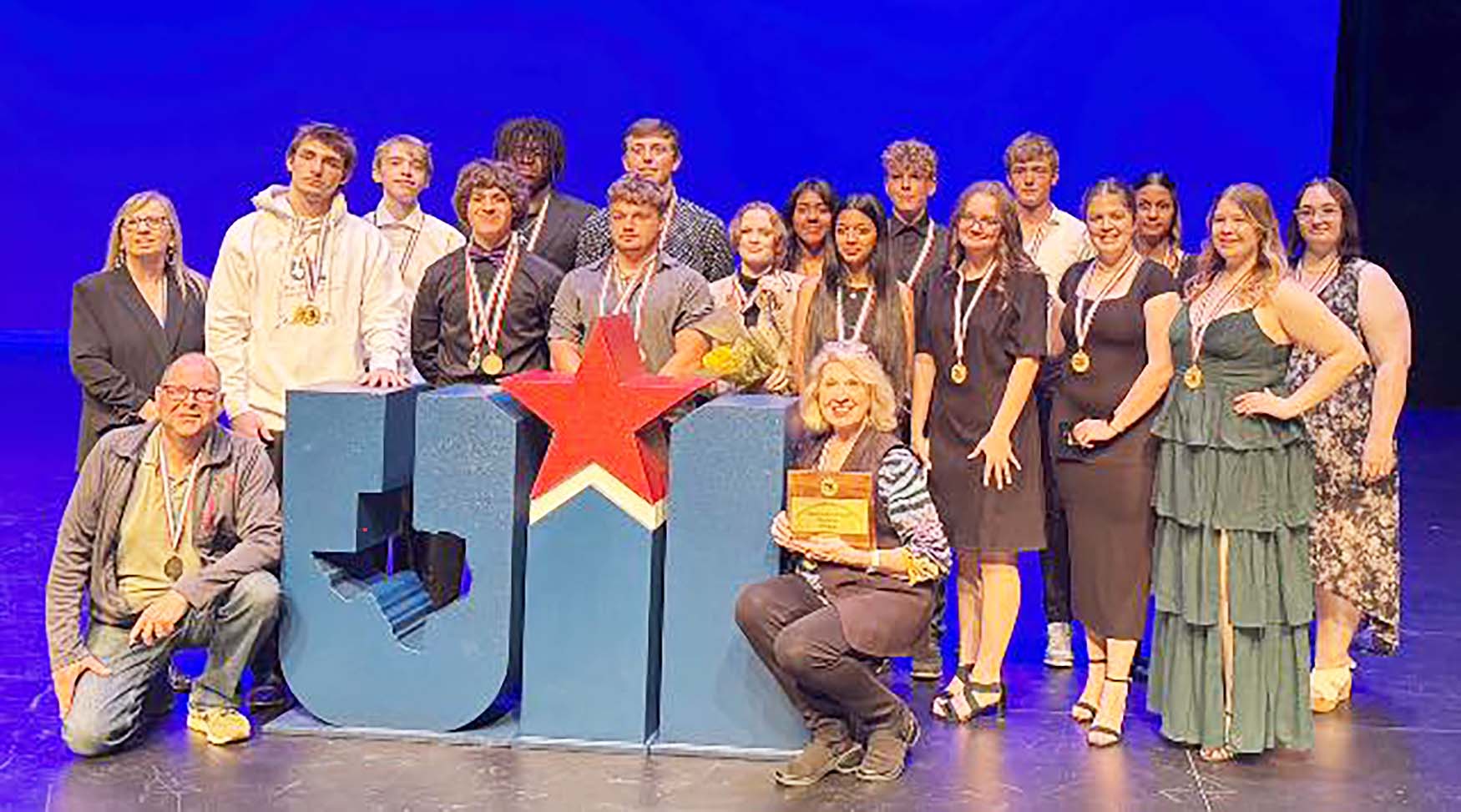
Gold-Burg one-act play earns spot in the state playbill

By BARBARA GREEN
[email protected]
Gold-Burg High School’s one-act play, “Interview,” advanced to state competition in Austin after an outstanding performance at regionals last Friday.
The Bears advance with eight other plays with a chance to take the state title on May 13. Students taking honors at regionals were Izzy Rohde who won Best All Around Female Performer. Director Linda Fitzner said Rohde is an eighth grader and they had to obtain permission for her to move up and participate in one-act.
Levi Hellinger and Barrett Allen won All Star Cast and Aidan Foster received a special individual lighting award. Jimena Garcia was honorable mention All Star Cast.
There will be a public show at 4 p.m. May 5 in the Bowie Junior High Auditorium.
For Gold-Burg this is their first time to take a one-act play to state. They have made it to regionals two or three other times, but it is the first for state.
Read the full story in the mid-week Bowie News.
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year ago2 hurt, 1 jailed after shooting incident north of Nocona
-

 NEWS6 months ago
NEWS6 months agoSuspect indicted, jailed in Tia Hutson murder
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoSO investigating possible murder/suicide
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoWreck takes the life of BHS teen, 16
-
 NEWS9 months ago
NEWS9 months agoMurder unsolved – 1 year later Tia Hutson’s family angry, frustrated with no arrest
-

 NEWS12 months ago
NEWS12 months agoSheriff’s office called out to infant’s death
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoBowie Police face three-hour standoff after possible domestic fight
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoDriver stopped by a man running into the street, robbed at knifepoint





