HEALTHY LIVING
Reduce your risk of another heart attack or stroke

COVID-19 pandemic highlights importance of maintaining healthy routines
(Family Features) After a heart attack or stroke, as many as 1 in 4 survivors will have another one. However, lifestyle changes and working closely with your doctor to manage your health may minimize the risk of a repeat event. Sticking to secondary prevention routines – by eating healthy, being active and taking medications as prescribed – is important as cases of COVID-19 increase.
“A heart attack or stroke is a very scary experience, and people try to avoid revisiting that difficult time,” said neurologist Lee Schwamm, MD, chair of the American Stroke Association and professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School “Unfortunately, the risk of a repeat stroke is high, and lifestyle changes to reduce a person’s risk are almost always necessary to reduce those odds.”
Up to 80% of second clot-related strokes and heart attacks may be prevented by making healthy choices. Consider these tips from the American Stroke Association’s secondary heart attack and stroke prevention initiative, sponsored nationally by Bayer.
Blood Pressure: Work with your doctor to ensure you’re maintaining a healthy blood pressure level below 130/80. High blood pressure is both a leading cause and major risk factor for stroke and heart attack.
Cholesterol: Medication and healthy lifestyle habits can help keep high cholesterol in check.
Blood Sugar: Having diabetes, which is caused by high blood sugar, more than doubles your risk of stroke. Some people have diabetes and don’t know it until a medical emergency happens.
Medications: If you are prescribed medications for high blood pressure, high cholesterol or diabetes, make sure you take them as prescribed. If you had a clot-related stroke or a heart attack, your doctor may recommend aspirin to help prevent another event. Aspirin is not appropriate for everyone, so talk to your doctor before beginning an aspirin regimen.
Smoking: If you smoke, stop. Smoking increases the risk of stroke and heart attack because it damages blood vessels, which can lead to blockages.
Physical Activity: Being physically active at least 30 minutes a day, most days of the week or 150 minutes per week is recommended by the American Stroke Association.
Even as COVID-19 cases strain emergency medicine, calling 9-1-1 still provides access to life-saving treatments for people experiencing medical emergencies like heart attacks or strokes. Emergency medical responders can assess symptoms, begin treatment and transport the patient to the most appropriate hospital, if necessary.
Based on current information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, it appears people 65 and older and people of any age with underlying medical conditions, such as heart disease, high blood pressure and diabetes, are more likely to be infected and develop more severe symptoms. Stroke survivors may face increased risk for complications if they get COVID-19.
Know the Warning Signs for Strokes and Heart Attacks
Even as COVID-19 cases strain emergency medicine, experts say calling 9-1-1 is still the best way to access life-saving treatments for people who are experiencing heart attack or stroke symptoms.
Heart attacks and strokes are medical emergencies. If someone is experiencing stroke or heart attack symptoms, he or she should call 9-1-1. Emergency medical responders can assess symptoms, begin treatment in the ambulance and transport the patient to the most appropriate hospital, if necessary.
Hospitals have plans in place to keep potentially contagious patients away from others and keep surfaces clean. Calling 9-1-1 and activating Emergency Medical Services (EMS) ensures you have the best possible chance to beat a heart attack or stroke. EMS can begin treatment in the ambulance and take you to the hospital best suited to care for you in an emergency.
Stroke warning signs can be remembered using the acronym F.A.S.T.:
- F – Face drooping
- A – Arm weakness
- S – Speech difficulty
- T – Time to call 9-1-1
Heart attack warning signs include:
- Chest discomfort.
- Discomfort in other areas of the upper body such as one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw or stomach.
- Shortness of breath.
- Breaking out in a cold sweat
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness
Find more resources to help manage your risk at stroke.org/oneisenough.
Photo courtesy of Getty Images
SOURCE:
American Stroke Association
HEALTHY LIVING
Save a life from stroke

(Family Features) Strokes can happen to anyone, at any age – even young people. Despite being one of the leading causes of death and long-term disability in the United States, strokes are largely preventable, treatable and beatable – if you can control your risk factors.
According to the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association, every 40 seconds, someone in the U.S. has a stroke. Keeping blood pressure in check, living a healthy lifestyle and knowing stroke warning signs may help protect you and your loved ones.
Here are key insights from the American Stroke Association’s Together to End Stroke initiative, nationally supported by the HCA Healthcare Foundation.
Controlling Risk Factors
Up to 80% of strokes may be preventable, according to the American Stroke Association. You can take action to prevent strokes by managing your risk factors, like high blood pressure, a leading cause and controllable risk factor for stroke and heart disease.
Other risk factors include diabetes and obesity, which can be kept in check with healthy lifestyle behaviors such as good nutrition. Quitting smoking and being physically active are important. Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, which is a quivering or irregular heartbeat, also increases stroke risk. In fact, people with AFib are five times more likely to have a stroke, according to the American Heart Association.
Preventing a Second Stroke
Nearly 1 in 4 strokes occur in people who had a previous stroke, sometimes because they don’t know what caused the first, making identifying the cause of the stroke a key step toward future prevention. Treatment depends on the type of stroke someone is having, which can be determined with a series of medical evaluations and tests.
Work with your health care professional to develop a plan that helps you move forward after a first stroke while preventing a second. This plan should include controlling risk factors, like achieving and maintaining healthy blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
“Preventing a second stroke is possible with the right approach,” said Teresita Casanova, MD, HCA Healthcare affiliated neurologist and American Stroke Association volunteer expert. “Taking medicines as prescribed, monitoring health numbers, and making small, consistent lifestyle changes can make a big difference. Stroke survivors should feel empowered to take control of their health and work with their care team to build a strong prevention plan.”
To help you in your journey, you can rely on tools such as the Heart & Stroke Helper, a free self-management app available for stroke survivors and their caregivers. The app allows patients to oversee their health in one place with features that track progress on lifestyle habits, manage medications, track health numbers, provide information about stroke and allow patients to connect with others for inspiration.
Find more ways to manage second stroke risk at Stroke.org

Act F.A.S.T.: How to Detect Signs of Stroke
Most adults in the U.S. don’t know the stroke warning signs, nor that stroke is largely treatable if you call 911 as soon as you recognize the symptoms.
Learning the acronym F.A.S.T. can help you recognize that someone may be having stroke symptoms so you can take life-saving action.
F: Face Drooping. Does one side of the face droop, or is it numb? Ask the person to smile. Is the person’s smile uneven?
A: Arm Weakness. Is one arm weak or numb? Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
S: Speech. Is speech slurred? Is the person unable to speak or hard to understand? Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence, like “The sky is blue.”
T: Time to Call 911. If you or anyone else shows any of these symptoms, call 911 immediately.
Photo courtesy of Shutterstock
SOURCE:
HEALTHY LIVING
How to conduct a skin care self-exam
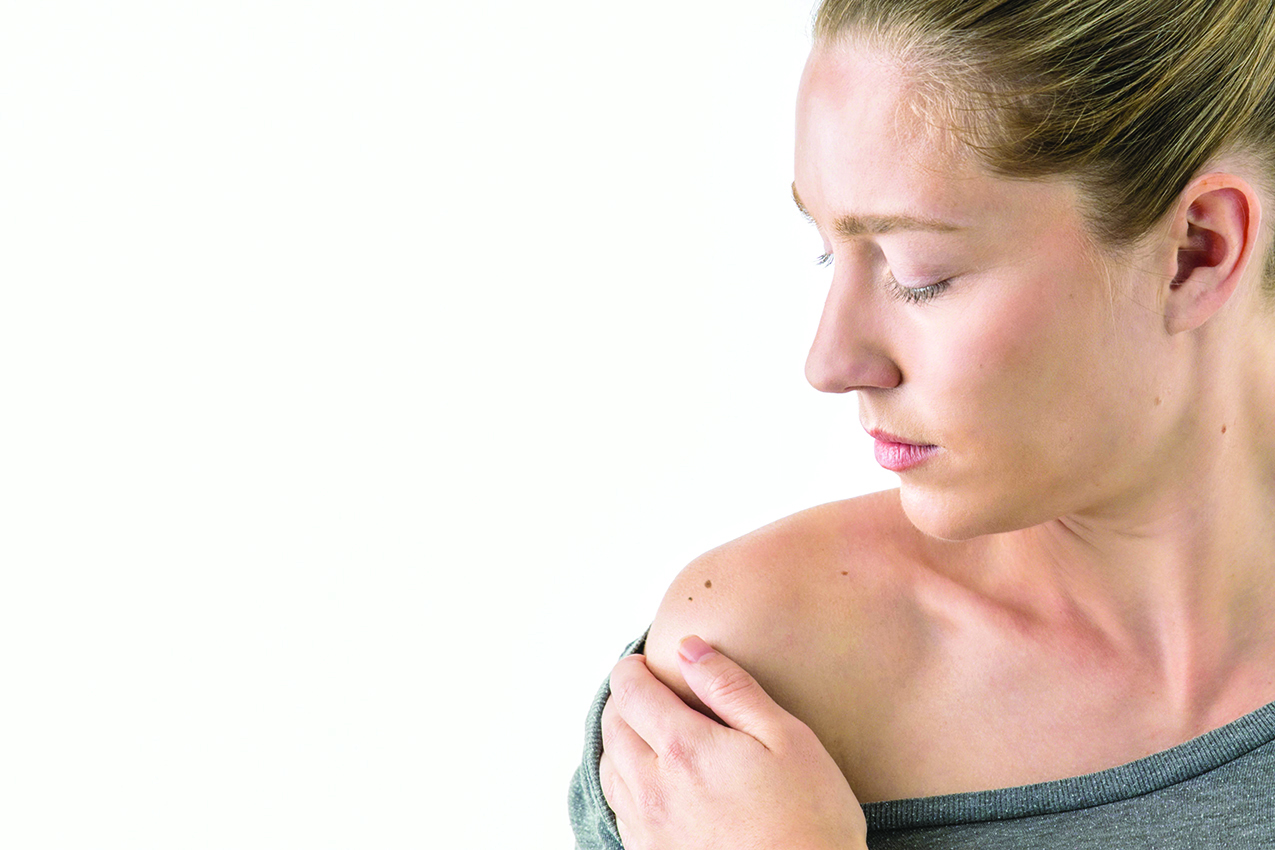
Time spent soaking up the summer sun is one of the things that makes the season so appealing. Warm outdoor air has a calming effect that can make anyone feel more relaxed and comfortable.
As good as warm summer sun can feel, overexposure to the sun can be dangerous. The World Cancer Research Fund reports there were more than 330,000 new cases of skin cancer diagnosed across the globe in 2022. A significant percentage of skin cancer cases can be prevented, and prevention is a multifaceted process that includes skin care self-examinations. Self-exams do not take up much time, and individuals can speak with their physicians about how frequently they should check their skin for signs of skin cancer. The U.S. National Library of Medicine offers the following instructions for how to conduct a skin self-exam.
Choose the right time to examine your skin. The USNLM recommends conducting a skin exam after bathing. Women who routinely conduct breast self-exams can check their skin at this time as well.
Use a full-length mirror. ItÕs not always easy to examine skin throughout the body. But signs of skin problems can occur anywhere on the body, including areas that might be hard to see without help. If possible, conduct a self-exam of the skin in front of full-length mirror in a brightly lit room.
Identify what youÕre looking for. The USNLM notes you should be looking for any new skin markings. This includes bumps, moles, blemishes, and changes in skin color.
Pay close attention to preexisting moles. A potential sign of skin cancer includes moles that change over time. Examine preexisting moles to see if they have changed in size, texture, color, and shape.
Look for unusual moles. The USNLM characterizes certain moles as Òugly duckling moles.Ó These unique moles look and feel different from nearby moles and may be indicative of skin cancer. Speak with a dermatologist if a self-exam uncovers the presence of moles with uneven edges or differences in colors or asymmetric shapes. Moles that look different from one side to the other also should be brought to the attention of a dermatologist. Moles that do not stop bleeding or will not heal also merit examination by a skin care professional.
When the time comes to conduct the exam, the USNLM recommends following these steps:
- Look closely at your entire body, both front and back, in the mirror.
- Check under your arms and on both sides of each arm. Be sure to examine the backs of your upper arms, which can be hard to see.
- Bend your arms at the elbow, and examine both sides of your forearm.
- Examine the tops and palms of your hands.
- Examine the front and back of both legs.
- Examine your buttocks and between your buttocks.
- Examine your genital area.
- Examine your face, neck, the back of your neck, and scalp. Use both a hand mirror and full-length mirror, along with a comb, to see areas of your scalp.
- Examine your feet, including the soles and the spaces between your toes.
- Ask a person you trust to help examine hard-to-see areas.
Skin cancer poses a formidable threat, but many cases of the disease are preventable. Routine skin self-exams are a vital component of skin cancer prevention. TF256909
HEALTHY LIVING
What does 100% grass-fed organic dairy bring to your table

(Family Features) It’s no secret that many grocery store dairy sections are filled with more options today. One choice continuing to gain favor with consumers is 100% grass-fed organic dairy. Nutrition, environmental awareness and animal care are some of the leading reasons consumers choose grass-fed dairy products.
Globally, the 100% grass-fed dairy market is projected to continue growing and some market experts predict annual growth rates as high as 22%. If you’re curious about 100% grass-fed organic dairy, consider these benefits from Maple Hill, America’s original 100% grass-fed organic dairy producer. The pioneer of 100% grass-fed organic dairy took its commitment a step further by celebrating and declaring National 100% Grass-Fed Organic Dairy Day on April 15, which recognizes the positive impact it has on consumers, cows, farmers and the environment.
1. Honoring the Farmers
Unlike large-scale corporate dairy farms, most organic farms are small, family-owned operations dedicated to traditional, sustainable farming. Small dairy farms have been disappearing, but 100% grass-fed organic dairy creates a sustainable, viable path forward for farmers who work in harmony with nature.
This more natural approach to dairy is a “craft” process favoring small family farmers who are willing to dedicate the extra focus and patience to a better product and process. These family farms are passed on to future generations to grow the “better for you, better for the planet” approach.
2. Commitment to Good Health
Most consumers don’t know the difference between traditional organic and 100% grass-fed organic dairy. One key distinction is the products’ nutritional composition; 100% grass-fed organic dairy provides a 50% healthier ratio of omega 3:6 and 40% higher levels of CLA fatty acids, which may support heart health and provide other health benefits.
What’s more, Maple Hill’s products made with 100% grass-fed organic dairy are GMO free, hormone free and antibiotic free with no additives or fillers. The line of high-quality, rich-flavored products let you experience the organic difference from traditional dairy for a nutrient-dense solution that tastes as nature intended.
3. Happy, Healthy Cows
Cows on a 100% grass-fed diet can live up to three times as long as grain-fed cows and are never subjected to unnatural diets, hormones or antibiotics. More time in pastures filled with lush grass means cows have the freedom to roam, ruminate and graze on diverse, nutrient-rich grasses.
The result is happier, healthier cows, which in turn results in a richer, better-tasting and more nutrient-dense milk.
4. Sustainability and the Environment
Producing milk without grain or corn requires farmers to focus on regenerating soil and the soil life that supports everything else on the farm. In fact, the healthier the soil, the healthier the feed, so farmers have a natural incentive to be as regenerative as possible. Regenerative grazing practices are a powerful and positive tool to improve land and the web of life on farms by actively restoring soil health, promoting biodiversity and reducing the environmental impact compared to conventional dairy.
Well-managed grazing helps pull carbon from the atmosphere into the soil, fighting climate change in the process. In addition, healthier soil retains more water, reducing runoff and protecting water sources from agricultural pollution.
5. Strengthening the 100% Grass-Fed Organic Market
Consumers are increasingly aware of the choices they have in dairy products and how 100% grass-fed organic supports their health, farmers, animals and the planet. Some ways to support this category’s continued growth include choosing certified 100% grass-fed organic dairy, advocating for regenerative farming and helping shape a more sustainable food system.
Learn more about 100% grass-fed organic dairy products at maplehill.com.
SOURCE:
-

 NEWS3 years ago
NEWS3 years ago2 hurt, 1 jailed after shooting incident north of Nocona
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSuspect indicted, jailed in Tia Hutson murder
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSO investigating possible murder/suicide
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoWreck takes the life of BHS teen, 16
-
 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoMurder unsolved – 1 year later Tia Hutson’s family angry, frustrated with no arrest
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSheriff’s office called out to infant’s death
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoBowie Police face three-hour standoff after possible domestic fight
-

 NEWS3 years ago
NEWS3 years agoDriver stopped by a man running into the street, robbed at knifepoint






