This Day In History
Michelangelo born

With the success of the Pieta, the artist was commissioned to sculpt a monumental statue of the biblical character David for the Florence cathedral. The 17-foot statue, produced in the classical style, demonstrates the artist’s exhaustive knowledge of human anatomy and form. In the work, David is shown watching the approach of his foe Goliath, with every muscle tensed and a pose suggesting impending movement. Upon the completion of David in 1504, Michelangelo’s reputation was firmly established.
That year, he agreed to paint a mural for the Florence city hall to rest alongside one being painted by Leonardo da Vinci, another leading Renaissance artist and an influence on Michelangelo. These murals, which depicted military scenes, have not survived. In 1505, he began work on a planned group of 12 marble apostles for the Florence cathedral but abandoned the project when he was commissioned to design and sculpt a massive tomb for Pope Julius II in Saint Peter’s Basilica in Rome. There were to have been 40 sculptures made for the tomb, but the pope soon ran out of funds for the project, and Michelangelo left Rome.
In 1508, he was called back to Rome to paint the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel–the chief consecrated space in the Vatican. Michelangelo’s epic ceiling frescoes, which took several years to complete, are among his most memorable works. Central in a complex system of decoration featuring numerous figures are nine panels devoted to biblical world history. The most famous of these is The Creation of Adam, a painting in which the arms of God and Adam are outstretched toward each other.
In 1512, Michelangelo completed the Sistine Chapel ceiling and returned to his work on Pope Julius II’s tomb. He eventually completed a total of just three statues for the tomb, which was eventually placed in the church of San Pietro in Vincoli. The most notable of the three is Moses (1513-15), a majestic statue made from a block of marble regarded as unmalleable by other sculptors. In Moses, as in David, Michelangelo infused the stone with a powerful sense of tension and movement.
Having revolutionized European sculpture and painting, Michelangelo turned to architecture in the latter half of his life. His first major architectural achievement was the Medici chapel in the Church of San Lorenzo in Florence, built to house the tombs of the two young Medici family heirs who had recently died. The chapel, which he worked on until 1534, featured many innovative architectural forms based on classical models. The Laurentian Library, which he built as an annex to the same church, is notable for its stair-hall, known as the ricetto, which is regarded as the first instance of mannerism as an architectural style. Mannerism, a successor to the Renaissance artistic movement, subverted harmonious classical forms in favor of expressiveness.
In 1534, Michelangelo left Florence for the last time and traveled to Rome, where he would work and live for the rest of his life. That year saw his painting of the The Last Judgment on a wall above the altar in the Sistine Chapel for Pope Paul III. The massive painting depicts Christ’s damnation of sinners and blessing of the virtuous, and is regarded as a masterpiece of early mannerism. During the last three decades of his life, Michelangelo lent his talents to the design of numerous monuments and buildings for Rome, which the pope and city leaders were determined to restore to the grandeur of its ancient past. The Capitoline Square and the dome of St. Peter’s, designed by Michelangelo but not completed in his lifetime, remain two of Rome’s most famous visual landmarks.
Michelangelo worked until his death in 1564 at the age of 88. In addition to his major artistic works, he produced numerous other sculptures, frescoes, architectural designs, and drawings, many of which are unfinished and some of which are lost. He was also an accomplished poet, and some 300 of his poems are preserved. In his lifetime, he was celebrated as Europe’s greatest living artist, and today he is held up as one of the greatest artists of all time, as exalted in the visual arts as William Shakespeare is in literature or Ludwig van Beethoven is in music.
– History.com Staff
This Day In History
Truman announces development of H-bomb

U.S. President Harry S. Truman publicly announces his decision to support the development of the hydrogen bomb, a weapon theorized to be hundreds of times more powerful than the atomic bombs dropped on Japan during World War II.
Five months earlier, the United States had lost its nuclear supremacy when the Soviet Union successfully detonated an atomic bomb at their test site in Kazakhstan. Then, several weeks after that, British and U.S. intelligence came to the staggering conclusion that German-born Klaus Fuchs, a top-ranking scientist in the U.S. nuclear program, was a spy for the Soviet Union. These two events, and the fact that the Soviets now knew everything that the Americans did about how to build a hydrogen bomb, led Truman to approve massive funding for the superpower race to complete the world’s first “superbomb,” as he described it in his public announcement on January 31.
On November 1, 1952, the United States successfully detonated “Mike,” the world’s first hydrogen bomb, on the Eniwetok Atoll in the Pacific Marshall Islands. The 10.4-megaton thermonuclear device, built upon the Teller-Ulam principles of staged radiation implosion, instantly vaporized an entire island and left behind a crater more than a mile wide. The incredible explosive force of Mike was also apparent from the sheer magnitude of its mushroom cloud–within 90 seconds the mushroom cloud climbed to 57,000 feet and entered the stratosphere. One minute later, it reached 108,000 feet, eventually stabilizing at a ceiling of 120,000 feet. Half an hour after the test, the mushroom stretched 60 miles across, with the base of the head joining the stem at 45,000 feet.
Three years later, on November 22, 1955, the Soviet Union detonated its first hydrogen bomb on the same principle of radiation implosion. Both superpowers were now in possession of the “hell bomb,” as it was known by many Americans, and the world lived under the threat of thermonuclear war for the first time in history.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/truman-announces-development-of-h-bomb
This Day In History
Gandhi assassinated
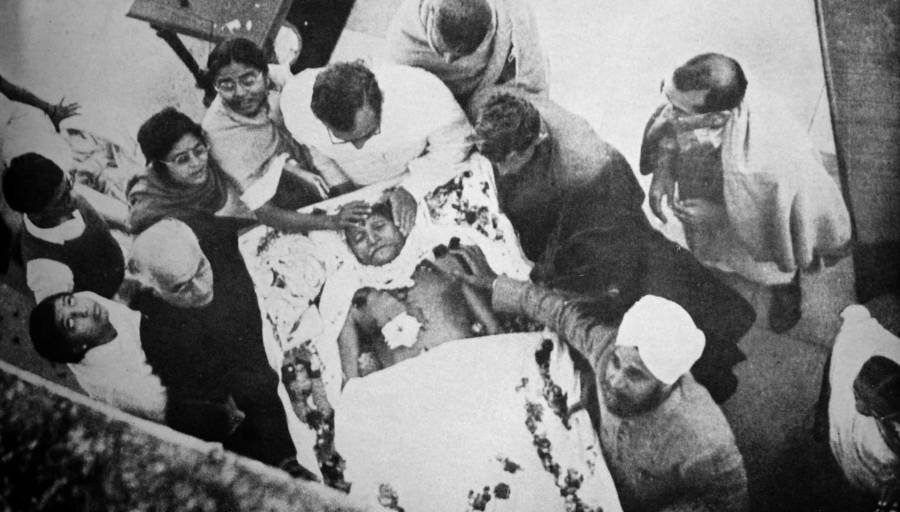

Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, the political and spiritual leader of the Indian independence movement, is assassinated in New Delhi by a Hindu extremist.
Born the son of an Indian official in 1869, Gandhi’s Vaishnava mother was deeply religious and early on exposed her son to Jainism, a morally rigorous Indian religion that advocated nonviolence. Gandhi was an unremarkable student but in 1888 was given an opportunity to study law in England. In 1891, he returned to India, but failing to find regular legal work he accepted in 1893 a one-year contract in South Africa.
Settling in Natal, he was subjected to racism and South African laws that restricted the rights of Indian laborers. Gandhi later recalled one such incident, in which he was removed from a first-class railway compartment and thrown off a train, as his moment of truth. From thereon, he decided to fight injustice and defend his rights as an Indian and a man. When his contract expired, he spontaneously decided to remain in South Africa and launched a campaign against legislation that would deprive Indians of the right to vote. He formed the Natal Indian Congress and drew international attention to the plight of Indians in South Africa. In 1906, the Transvaal government sought to further restrict the rights of Indians, and Gandhi organized his first campaign of satyagraha, or mass civil disobedience. After seven years of protest, he negotiated a compromise agreement with the South African government.
In 1914, Gandhi returned to India and lived a life of abstinence and spirituality on the periphery of Indian politics. He supported Britain in the First World War but in 1919 launched a new satyagraha in protest of Britain’s mandatory military draft of Indians. Hundreds of thousands answered his call to protest, and by 1920 he was leader of the Indian movement for independence. He reorganized the Indian National Congress as a political force and launched a massive boycott of British goods, services, and institutions in India. Then, in 1922, he abruptly called off the satyagraha when violence erupted. One month later, he was arrested by the British authorities for sedition, found guilty, and imprisoned.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/gandhi-assassinated
This Day In History
U.S. Baseball Hall of Fame elects first members
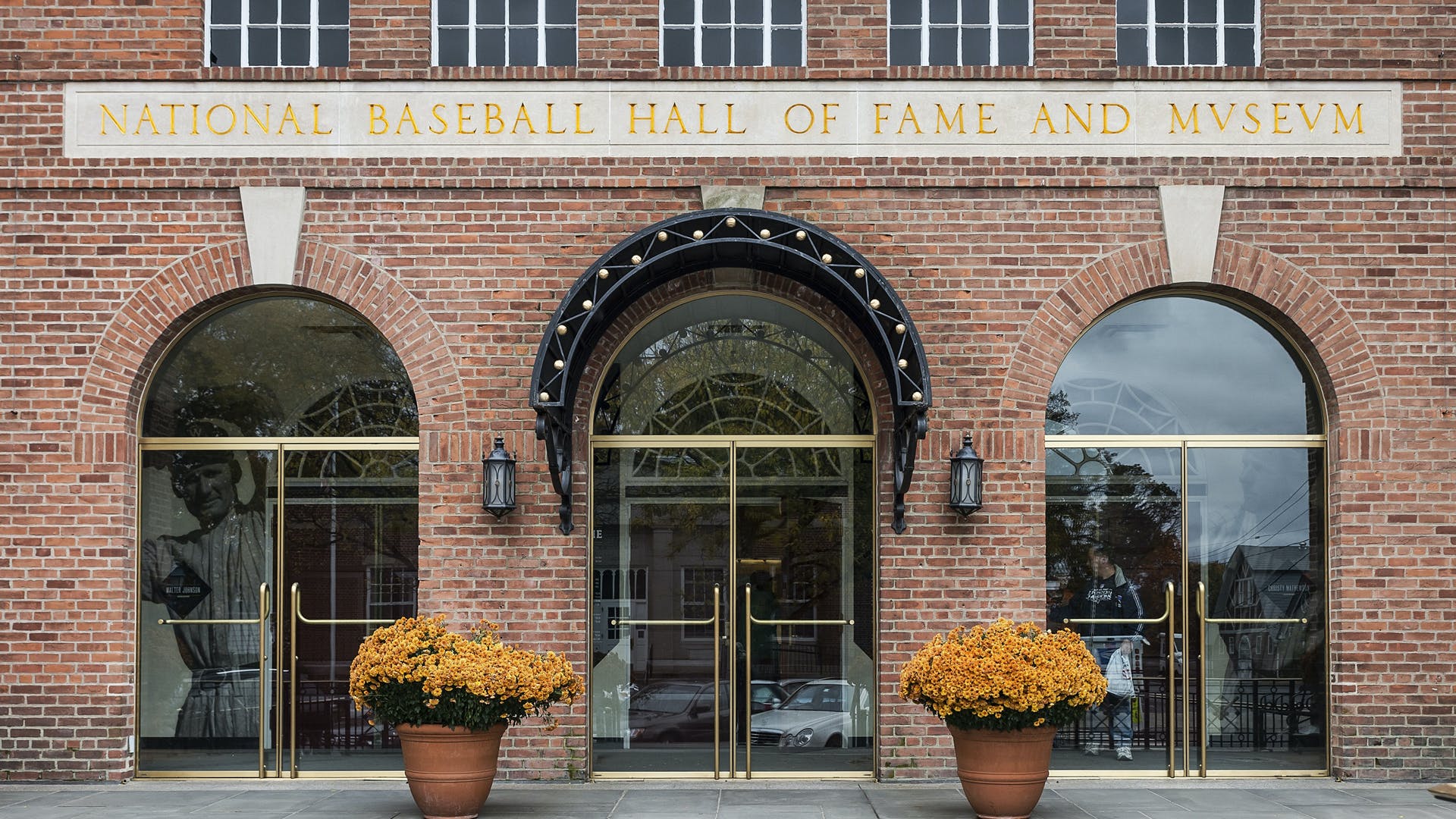

On January 29, 1936, the U.S. Baseball Hall of Fame elects its first members in Cooperstown, New York: Ty Cobb, Babe Ruth, Honus Wagner, Christy Matthewson and Walter Johnson.
The Hall of Fame actually had its beginnings in 1935, when plans were made to build a museum devoted to baseball and its 100-year history. A private organization based in Cooperstown called the Clark Foundation thought that establishing the Baseball Hall of Fame in their city would help to reinvigorate the area’s Depression-ravaged economy by attracting tourists. To help sell the idea, the foundation advanced the idea that U.S. Civil War hero Abner Doubleday invented baseball in Cooperstown. The story proved to be phony, but baseball officials, eager to capitalize on the marketing and publicity potential of a museum to honor the game’s greats, gave their support to the project anyway.
In preparation for the dedication of the Hall of Fame in 1939—thought by many to be the centennial of baseball—the Baseball Writers’ Association of America chose the five greatest superstars of the game as the first class to be inducted: Ty Cobb was the most productive hitter in history; Babe Ruth was both an ace pitcher and the greatest home-run hitter to play the game; Honus Wagner was a versatile star shortstop and batting champion; Christy Matthewson had more wins than any pitcher in National League history; and Walter Johnson was considered one of the most powerful pitchers to ever have taken the mound.
Today, with approximately 350,000 visitors per year, the Hall of Fame continues to be the hub of all things baseball.
Source: https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/u-s-baseball-hall-of-fame-elects-first-members
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year ago2 hurt, 1 jailed after shooting incident north of Nocona
-

 NEWS5 months ago
NEWS5 months agoSuspect indicted, jailed in Tia Hutson murder
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoSO investigating possible murder/suicide
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoWreck takes the life of BHS teen, 16
-
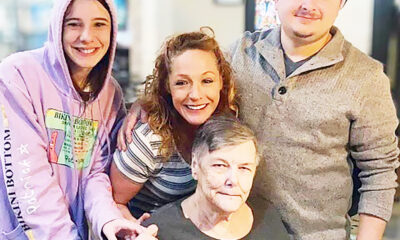
 NEWS9 months ago
NEWS9 months agoMurder unsolved – 1 year later Tia Hutson’s family angry, frustrated with no arrest
-

 NEWS12 months ago
NEWS12 months agoSheriff’s office called out to infant’s death
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoBowie Police face three-hour standoff after possible domestic fight
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoDriver stopped by a man running into the street, robbed at knifepoint





