HEALTHY LIVING
Going green in your community

(Family Features) Preserving your community for future generations can take many forms. It might mean volunteering with local organizations and participating in community improvement initiatives. Taking steps to protect the environment is another critical way to ensure your community remains safe and livable for generations to come.
These ideas show that going green can be as simple as making small modifications to everyday actions you already take.
Donating Unwanted Goods
Landfills are overflowing with items that still have plenty of useful life. Often, those discarded items could be repurposed to provide an affordable option to those who can’t afford new, full-price versions. Before loading up your trash can, consider donating things like household goods and clothing that could still serve a purpose. Numerous organizations accept gently used goods that they either distribute directly to those in need or sell to the general public, with proceeds benefiting a specific cause or population. Look into the options in your area to find the best fit for items you have that can be donated.
Rethinking Transportation Pollution from transportation accounts for 29% of the United States’ emissions, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). That’s a higher percentage than any other category measured by the EPA. Carpooling, public transportation and even carefully planning your route are ways you can take personal accountability to help reduce the problem.
Pollution from transportation accounts for 29% of the United States’ emissions, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). That’s a higher percentage than any other category measured by the EPA. Carpooling, public transportation and even carefully planning your route are ways you can take personal accountability to help reduce the problem.
Another way to improve transportation emissions is by talking to your school district about its school bus choices. Diesel school buses are not only expensive to operate, but they are harmful to children’s health, the community and the climate, according to data compiled by the Propane Education & Research Council. Conversely, propane reduces harmful emissions that impact student health and air quality in the community. By advocating for your district to convert to a more environmentally friendly transportation option, such as propane, you can help further reduce harmful emissions in your community.
Find more information about propane-powered buses at BetterOurBuses.com.
Recycling and Composting
Another way to reduce landfill waste is recycling and composting. Many of the items you throw away can be recycled into all-new materials. For example, recycled plastic can be used in a wide range of products, from sleeping bags and backpacks to dishes and reusable water bottles. Food waste represents a large share of landfills, too. Eventually it will biodegrade, but composting what you can at home gives you nutrient-rich material you can use to support your garden or lawn with healthier soil and less need for pesticides.
Cleaning with Natural Products
Keeping your home clean takes more than a little elbow grease, but the harsh chemicals found in many household cleaners are actually quite damaging. The chemicals can be poisonous or contain allergens that negatively impact your home’s air quality. Natural cleaners are often more cost-efficient, so you can enjoy cleaner air and minimize your impact on the environment.
Taking Advantage of Natural Light
If you’re in the habit of flipping on a light switch as you walk in a room, next time pause and consider whether you really need additional light. During daylight hours, many rooms offer more than enough natural light. Sunlight can also help warm spaces naturally when it’s cool outdoors, so throw open the curtains and let those warm, bright rays shine. If you do need additional light, consider relying on task lighting to illuminate your project rather than an overhead light that consumes more electricity.
Benefits of Propane School Buses
 Over the last several decades, there have been many advances in student transportation. However, one area that could still use improvement is the number of students who ride to school on diesel buses that pollute the air. Today, there are two meaningful energy choices for clean student transportation: propane and electric. While both can achieve clean transportation, propane buses cost one-third the price of electric, allowing districts to replace their aging diesel fleet faster.
Over the last several decades, there have been many advances in student transportation. However, one area that could still use improvement is the number of students who ride to school on diesel buses that pollute the air. Today, there are two meaningful energy choices for clean student transportation: propane and electric. While both can achieve clean transportation, propane buses cost one-third the price of electric, allowing districts to replace their aging diesel fleet faster.
As an affordable, available and clean energy source, propane buses make practical sense. The buses reduce harmful emissions by 96% compared to diesel. They can also meet school districts’ needs with a range of up to 400 miles and the resiliency to continue operating across all terrains and in any weather. In fact, more than 1,000 school districts have already made the switch. Every day, 1.3 million children ride to school in 22,000 propane school buses across the country.
In 2022, the EPA introduced the Clean School Bus Program, which provides $5 billion over five years (2022-26) to replace existing diesel school buses with zero-emission and low-emission models.
Through three rounds of funding, the EPA program has allocated more than $2.8 billion for 8,427 electric school buses and 440 low-emissions propane buses. However, for the same amount of money that was distributed for the electric buses (about $2.77 billion), the program could have helped fund as many as 92,635 propane buses, assuming each propane bus received the $30,000 incentive.
When considering full lifecycle emissions, replacing 92,635 diesel buses with propane buses would have reduced harmful nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by 24,664 metric tons over the three years the program has funded buses. By comparison, replacing just 8,427 diesel buses with electric buses will reduce NOx emissions by just 2,379 metric tons over the three years.
HEALTHY LIVING
Pediatric growth hormone deficiency (PGHD) 101

What parents should know about pediatric growth hormone deficiency
(Family Features) Pediatric growth hormone deficiency (GHD) is a relatively rare condition, affecting an estimated 1 in 4,000-10,000 children. Despite its rarity, GHD can significantly impact a child’s growth and development, which can potentially lead to short stature, delayed puberty, decreased muscle mass, delay in bone maturation and psychosocial implications.
With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, children with GHD can achieve improved growth outcomes and lead healthy lives. Increasing understanding of GHD treatment options and closing knowledge gaps can make a difference in the patient and caregiver journey.
What is PGHD?
Growth hormone plays a critical role in helping young bodies grow and develop, including improving muscle metabolism, growing bones and breaking down fats.
PGHD occurs when a child’s pituitary gland is unable to produce enough growth hormone which results in noticeable changes on the growth chart.
Children with PGHD may look younger than their peers of the same age and gender, and puberty may be delayed or absent. Muscle development, metabolism and bone strength may also be impacted by insufficient or inadequate levels of growth hormone.
While growth hormone stimulates height increase during development, its role in the body extends beyond childhood. Even after growth plates close, growth hormone plays a vital role for cardiovascular health and for maintaining normal body structure and metabolism. Research also indicates osteoporosis as a long-term implication of GHD, highlighting its importance in overall health and well-being.
What are the Symptoms?
PGHD may be apparent during infancy, or it may not be revealed until later in childhood. Children with PGHD tend to have typical body proportions but noticeably slow growth. Other symptoms may include an immature or significantly younger look than other children of the same age, chubby body build, slow hair and nail growth, teeth that come in late and episodes of low blood sugar.
Children who have experienced a brain injury, brain tumor or radiation treatment involving the head are at higher risk for PGHD. Genetic factors can also increase risk.
How are Children Diagnosed?
Generally, doctors attempt to rule out other causes of slow growth, which may include genetic short stature, poor nutrition – which may be the result of an underlying condition such as celiac disease – and other genetic conditions, such as a hypothyroidism or Turner syndrome.
X-rays to evaluate bone age and imaging to identify the location of the pituitary gland can support the diagnosis. Another common screening option is a growth hormone stimulation test, in which medications are administered to trigger the release of growth hormone and blood is drawn frequently to monitor the body’s response.
What Treatment Options are Available?
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, children with PGHD often work closely with an endocrinologist to develop a treatment plan that includes growth hormone replacement therapy and closely monitor future growth. Dosing is based on weight and requires ongoing monitoring for adjustments. Traditionally, treatment was through daily injections, but more recently, weekly injections became available.
Children with PGHD who begin treatment early in life are more likely to reach adult height consistent with their family’s stature.
Learn more about PGHD at GHDinKids.com.

From Playdate to PGHD
During a visit to a friend’s house, Erin Swieter noticed her 18-month-old daughter, Ingrid, was about a head shorter than her peer who was six weeks younger. Upon learning her friend’s daughter was only in the 10th percentile for height, Swieter realized Ingrid must be even smaller.
While she was hitting her developmental milestones, she was still wearing 9-to-12-month clothes and had a baby-like appearance. Swieter took her concerns to Ingrid’s pediatrician; her growth charts were monitored closely for the next several months.
Following a move to a new city, the Swieters found a new pediatric endocrinologist, who was instrumental in diagnosing Ingrid. The endocrinologist reviewed previous labs and monitored Ingrid’s growth carefully, eventually diagnosing her with PGHD after a failed growth hormone stimulation test.
“Receiving Ingrid’s diagnosis was a relief, as it confirmed our suspicions and gave us a clear path forward,” Swieter said.
After learning about daily injections, the Swieters were hesitant about proceeding. The Swieters discussed their worries with Ingrid’s pediatric endocrinologist, who recommended weekly injections as a viable option due to Ingrid’s age and the duration of treatment she would likely need.
“We had heard from other parents about the challenges of daily medications, which could pose a problem during travel, day trips or sleepovers at Grandma’s house,” Swieter said. “The weekly injection eliminates the need for a daily treatment routine.”
Navigating the insurance approval process proved challenging, but once Swieter provided evidence of two failed growth hormone stimulation tests, the weekly injections were approved.
“Insurance and pharmacy challenges can be frustrating, but patience and persistence are key,” Swieter said. “Educate yourself about your insurance, treatment options, and medical literature to be a strong advocate for your child.”
Ingrid has embraced opportunities to share her journey with her condition through a school project, proudly engaging her classmates in conversations about her experience. At the same time, she is making strides physically, continuing to grow and thrive.
Photos courtesy of Shutterstock (mom measuring daughter and mom and son talking to doctor)
Real patient and caregiver photo courtesy of Erin Swieter (mom and daughter hiking)
SOURCE:
HEALTHY LIVING
Understanding the hidden dangers of LDL (Bad) Cholesterol

(Family Features) These days, wellness information is practically everywhere you turn. Do this; don’t do that. Eat more of this; eat less of that. This is good for you; that is bad.
It can be hard to cut through all the noise, but the reality is, when it comes to something as serious as your heart health and LDL cholesterol – the “bad” cholesterol – ignoring it can be downright dangerous for your health.
According to the American Heart Association, about every 40 seconds, someone in the United States has a heart attack, and strokes occur at about the same frequency.
High LDL cholesterol, often called “bad” cholesterol, significantly increases your risk of heart disease.
A poll conducted by The Harris Poll for the American Heart Association revealed 75% of heart attack and stroke survivors reported having high cholesterol. Yet nearly half (47%) of heart attack and stroke survivors are unaware of their LDL cholesterol number. This lack of awareness shows more knowledge is needed to help survivors proactively manage their health.
In fact, knowledge is key to reducing your risk of heart disease. Understanding the impact of LDL cholesterol and knowing your LDL number can help you make informed decisions.
Cholesterol: The Good and The Bad
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance your body needs to build cells and produce hormones. However, not all cholesterol is created equal:
- LDL (low-density lipoprotein) Cholesterol: This is the “bad” cholesterol. When too much LDL cholesterol circulates in the blood, it can build up in the inner walls of the arteries that feed the heart and brain, forming plaque that can narrow and eventually block these arteries, leading to heart attack or stroke.
- HDL (high-density lipoprotein) Cholesterol: Known as the “good” cholesterol, HDL helps remove the “bad” cholesterol from the arteries, protecting against heart attack and stroke.
A Silent Threat
Many people think high cholesterol has obvious signs, but that’s not always the case. In fact, about half of U.S. adults and 42% of heart attack and stroke survivors mistakenly believe high cholesterol has clear symptoms. However, high LDL cholesterol typically doesn’t show any signs, which is why it’s known as a silent threat to your heart.
People who have had a heart attack or stroke are at higher risk of future cardiovascular problems, which is why it’s important to monitor your cholesterol regularly to help prevent future events.
It’s also important to know high LDL cholesterol can be genetic, meaning someone who eats a healthy diet and exercises regularly can still have high cholesterol. Additionally, the risk of high LDL cholesterol increases with age.
That’s why the American Heart Association’s “Lower Your LDL Cholesterol Now” initiative, nationally sponsored by Amgen, emphasizes the importance of regular cholesterol checks regardless of your weight, diet and physical activity levels. Knowing your LDL cholesterol number – and understanding the target levels based on your health history – gives you the opportunity to manage your health proactively. This enables you to make informed decisions to prevent future heart issues.
Know Your Number
You can reduce your risk of a heart attack or stroke by knowing and addressing your LDL cholesterol number.
Working closely with your doctor allows you to actively manage high LDL cholesterol – often a key risk factor you can help control – and together, you can develop a personalized treatment plan. Ask your doctor or health care provider for a cholesterol test to know your LDL number. Understanding your cholesterol number is the first step toward managing it effectively. If necessary, appropriate management of your LDL cholesterol can help reduce your risk of a heart attack or stroke.
Your doctor may also talk with you about your personal and family medical history; previous heart-related medical events such as a heart attack or stroke; lifestyle habits such as tobacco use, obesity, unhealthy living or aging; racial and ethnic backgrounds; and reproductive health.
Lower is Better
When it comes to your cholesterol, guidelines from the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology recommend “lower is better” to reduce your risk. Studies show that an LDL number or below 100 mg/dL is ideal for healthy adults.
If you have a history of heart attack or stroke and are already on a cholesterol-lowering medication, your doctor may aim for your LDL to be 70 mg/dL or lower.
Talk to your doctor about the right treatment plan for you. Positive lifestyle habits, such as exercising and eating a healthy diet, may also help.
However, if you’ve had a heart attack or stroke before, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to lower your risk of another event. Your doctor may recommend cholesterol-lowering medications to protect your heart health.
Learn more about LDL (bad) cholesterol by visiting heart.org/LDL.
SOURCE:
HEALTHY LIVING
Save a life from stroke
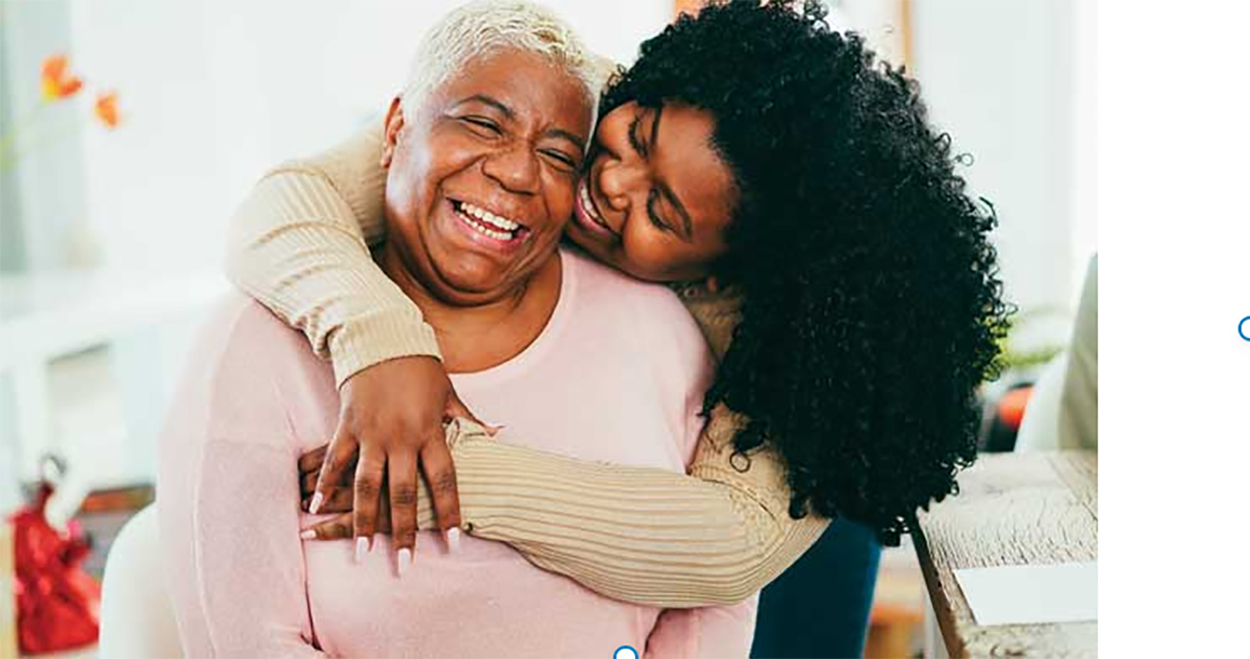

(Family Features) Strokes can happen to anyone, at any age – even young people. Despite being one of the leading causes of death and long-term disability in the United States, strokes are largely preventable, treatable and beatable – if you can control your risk factors.
According to the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association, every 40 seconds, someone in the U.S. has a stroke. Keeping blood pressure in check, living a healthy lifestyle and knowing stroke warning signs may help protect you and your loved ones.
Here are key insights from the American Stroke Association’s Together to End Stroke initiative, nationally supported by the HCA Healthcare Foundation.
Controlling Risk Factors
Up to 80% of strokes may be preventable, according to the American Stroke Association. You can take action to prevent strokes by managing your risk factors, like high blood pressure, a leading cause and controllable risk factor for stroke and heart disease.
Other risk factors include diabetes and obesity, which can be kept in check with healthy lifestyle behaviors such as good nutrition. Quitting smoking and being physically active are important. Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, which is a quivering or irregular heartbeat, also increases stroke risk. In fact, people with AFib are five times more likely to have a stroke, according to the American Heart Association.
Preventing a Second Stroke
Nearly 1 in 4 strokes occur in people who had a previous stroke, sometimes because they don’t know what caused the first, making identifying the cause of the stroke a key step toward future prevention. Treatment depends on the type of stroke someone is having, which can be determined with a series of medical evaluations and tests.
Work with your health care professional to develop a plan that helps you move forward after a first stroke while preventing a second. This plan should include controlling risk factors, like achieving and maintaining healthy blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
“Preventing a second stroke is possible with the right approach,” said Teresita Casanova, MD, HCA Healthcare affiliated neurologist and American Stroke Association volunteer expert. “Taking medicines as prescribed, monitoring health numbers, and making small, consistent lifestyle changes can make a big difference. Stroke survivors should feel empowered to take control of their health and work with their care team to build a strong prevention plan.”
To help you in your journey, you can rely on tools such as the Heart & Stroke Helper, a free self-management app available for stroke survivors and their caregivers. The app allows patients to oversee their health in one place with features that track progress on lifestyle habits, manage medications, track health numbers, provide information about stroke and allow patients to connect with others for inspiration.
Find more ways to manage second stroke risk at Stroke.org

Act F.A.S.T.: How to Detect Signs of Stroke
Most adults in the U.S. don’t know the stroke warning signs, nor that stroke is largely treatable if you call 911 as soon as you recognize the symptoms.
Learning the acronym F.A.S.T. can help you recognize that someone may be having stroke symptoms so you can take life-saving action.
F: Face Drooping. Does one side of the face droop, or is it numb? Ask the person to smile. Is the person’s smile uneven?
A: Arm Weakness. Is one arm weak or numb? Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
S: Speech. Is speech slurred? Is the person unable to speak or hard to understand? Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence, like “The sky is blue.”
T: Time to Call 911. If you or anyone else shows any of these symptoms, call 911 immediately.
Photo courtesy of Shutterstock
SOURCE:
-

 NEWS3 years ago
NEWS3 years ago2 hurt, 1 jailed after shooting incident north of Nocona
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSuspect indicted, jailed in Tia Hutson murder
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSO investigating possible murder/suicide
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoWreck takes the life of BHS teen, 16
-
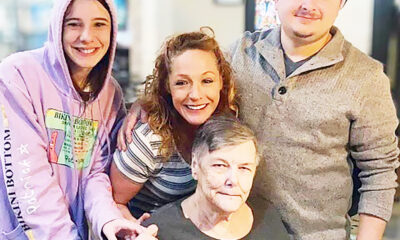
 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoMurder unsolved – 1 year later Tia Hutson’s family angry, frustrated with no arrest
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSheriff’s office called out to infant’s death
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoBowie Police face three-hour standoff after possible domestic fight
-

 NEWS3 years ago
NEWS3 years agoDriver stopped by a man running into the street, robbed at knifepoint






