Live Better
Tree talk: Tips for planting trees

4 tips for planting trees
(Family Features) Trees are virtually everywhere you turn, from your own backyard to nearby parks and forests where you enjoy hiking. They provide shade and beauty, and some even bear fruit. Beyond all the immediate benefits, you may be surprised to discover trees are also a critical key to the future.
These facts and tips from the book “Now is the Time for Trees” offer practical insight on the importance of trees and how to nurture one from selection to planting and beyond.
A compelling and ever-growing body of evidence generated by scientists, health care professionals, conservationists, humanitarians and both public and private corporations supports the critical importance of trees and their impact on the human condition. Trees filter pollutants out of the air and water and provide protection for people and communities from dangerous heat and flooding. They lower urban temperatures, reduce energy bills and sequester carbon to slow the rate of climate change.
When you plant a tree in your yard or neighborhood, that tree goes to work filtering out pollutants, intercepting stormwater and capturing carbon. With proper placement, that tree can also help lower household energy use by as much as 20%.
You can engage in the tree planting movement and make a difference by planting trees around your home and surrounding community with these tips.
Consider the Growing Region
Choosing a tree that will flourish in your growing region is fundamental to becoming a successful tree planter. Start by getting familiar with the growing conditions of your planting site, including factors like sunlight, soil condition and room to grow.
The amount of available sunlight at your planting location will determine which tree species will be successful. Most trees require full sunlight for proper growth and flowering. Some do well in (or even prefer) partial or light shade, but few perform well in dense shade.
Before you plant, get your soil tested by a lab to evaluate what’s happening underground. Test results, which are usually returned in a couple of weeks, provide a complete analysis of nutrients, possible contamination and pH (alkalinity or acidity), as well as directions for correcting problems.
Be conscious of overhead or underground utilities, pavement, buildings, other trees, traffic intersections and other factors that may impact your planting space.
Shopping for a Tree
When choosing which kind of tree to plant, be conscious of details like size, flowering, color (including how colors may vary through the seasons) and your view from inside the house. While shopping, you can rely on plant labels to learn details about a tree’s growth pattern, sun requirements, watering needs and soil requirements.
Two common styles of trees are container-grown trees, which spend their entire nursery lives growing in a container, and ball-and-burlap trees, which grow in the ground until they achieve a targeted size.
A well-tended container-grown tree has been carefully monitored and moved into larger containers as the plant grows. Be wary of a tree with roots that circle or twist within the container, which may cause roots to die. For a ball-and-burlap tree, look for a firm, securely tied root ball that is large enough to support the mature tree; it should be about 10-12 inches wide for every inch of trunk diameter.
Prepare Your Planting Site
Properly preparing your planting site is one of the best things you can do to get your tree off to a strong start. Before you plant, make sure your tree is thoroughly hydrated by watering the container or root ball several hours before proceeding. When planting a tree into a lawn, remove a circle of grass at least 3 feet in diameter where the tree will go to reduce competition between turf and fine tree roots.
Start Digging
Dig a broad, shallow planting hole with gently sloping sides 3-4 times wider than the diameter of the root mass and the same depth. Mound removed soil on a tarp for easy backfilling. Loosening the soil on the sides of the hole allows roots to easily expand and establish faster, but don’t disturb soil at the bottom of the hole.
Once the tree is positioned, replace the soil while firmly but gently tamping the original soil around the base of the root ball to stabilize it. Create a water-holding basin around the tree by building up a ring of soil and water to settle roots. Spread protective mulch 2-4 inches deep in a 3-foot diameter around the base of the tree, but not touching the trunk.
Find more tips to successfully plant and care for your trees at arborday.org.
A Handy Guide for Planting Trees
A rally cry against climate change, “Now is the Time for Trees” is an inspirational and informative guide that explains the important role trees can play in preserving the environment.
Author Dan Lambe, CEO of the Arbor Day Foundation, offers compelling reasons to plant more trees while providing simple, actionable steps to get involved, choose the right tree and achieve planting success. For each book sold, the foundation will plant a tree in a forest in need.
Pick up a copy wherever books are sold or visit arborday.org/TimeforTreesBook.
The Power of Trees
From backyards to tropical rain forests, trees provide the necessities of life. Trees clean air and water, provide habitats for wildlife, connect communities and support human health.
- Trees are a proven affordable, natural way to pull carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere.
- Trees filter water and slow storm surge and flooding in cities.
- Trees provide shade, cooling cities by up to 10 degrees, which can help prevent heat-related deaths.
- Neighborhood trees can reduce stress, improve overall health in children and encourage physical activity.
- Trees support wildlife and aquatic life by providing habitats and helping keep waterways healthy, which ensures ecosystem balance and promotes biodiversity.
- Trees and other forest life work together to ensure a clean source of drinking water, buffer against extreme weather, provide medicines, offer outdoor recreation and enrich human culture.
Photos courtesy of Getty Images
SOURCE:
Arbor Day Foundation
Live Better
Physical movement can help fight chronic diseases
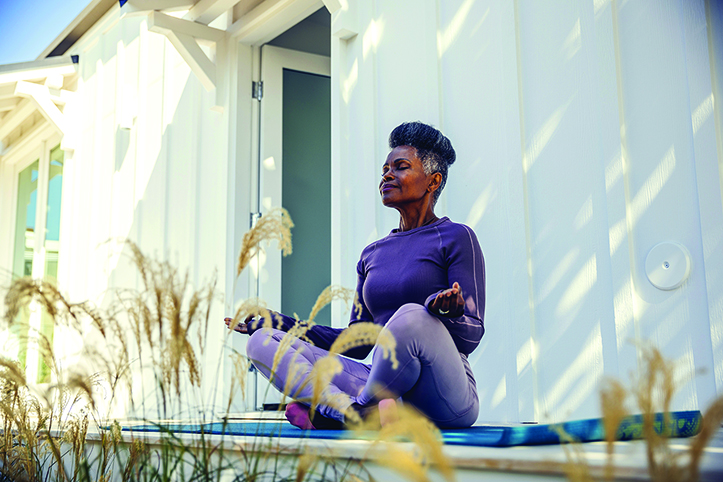

Physical activity is a valuable tool in the fight against chronic disease and other conditions. In fact, the Cleveland Clinic highlights physical activity among its nine ways to prevent disease in an effort to live a long and rewarding life.
Children, adolescents, young adults, and even men and women in middle age may not face too many physical hurdles when they try to exercise, but seniors are not always so lucky. Aging men and women with mobility issues may wonder if they can reap the rewards of physical activity, and thankfully there are many ways to exercise even if getting up and going isn’t as easy as it might have been in years past. Sometimes referred to as “aerobic exercise” or simply “cardio,” cardiovascular exercise is an umbrella term that encompasses a wide range of physical activities that raise the heart rate and improve endurance. Seniors with mobility issues can look to various forms of cardio for inspiration as they seek to be more physically active without compromising their overall health.
· Walk your way to a healthier you. Walking is a form of cardiovascular exercise that is ideal for older adults with mobility issues because it need not be physically demanding and it’s safe to walk just about anywhere. Walking in a place such as a local park can be particularly good for older adults because they can take periodic breaks on benches if aches, pains or stiffness is affecting their ability to keep moving.
· Take up swimming. Swimming might be tailor-made for seniors with mobility issues because it’s a great workout and exercising in water tends to be less taxing on muscles and joints. The Cleveland Clinic notes that swimming promotes heart health, strengthens the lungs, helps to burn calories, and builds muscle, among other benefits. And many seniors find swimming is just as fun in their golden years as it was in their youth, which means aging adults might not face problems with motivation when the time comes to get in the pool.
· Use an exercise bike or portable pedal exerciser. Cycling is a wonderful exercise but one that seniors with mobility issues may feel is no longer possible. If doctors advise against riding a traditional bike, an exercise bike or portable pedal exerciser can provide many of the benefits of cycling without as great a risk for accident or injury. A portable pedal exerciser can be carried to a park, where seniors can still spend time in the great outdoors, which is one of the most appealing reasons to get on a bike and go.
· Take beginner yoga or tai chi. HelpGuide.org notes that gentle yoga or tai chi can help to improve flexibility and reduce stress and anxiety. Though yoga and tai chi can provide as much demanding physical activity as individuals allow, beginner classes in each discipline don’t require much movement but do provide enough for seniors hoping to be less sedentary.
Even seniors with mobility issues can find safe and effective ways to be more physically active. Prior to beginning a new exercise regimen, seniors with mobility issues are urged to discuss activities with their physicians.
Live Better
Connected communities: Reducing the impact of isolation in rural areas

(Family Features) Throughout history, humans’ ability to rely on one another has been crucial to survival. Despite modern developments that help individuals live with minimal human engagement, the human need to connect remains.
However, in many parts of America, a trend toward isolation is emerging. Over the past two decades, people are spending more time alone and less time engaging with others in person, according to data from the Office of the U.S. Surgeon General. One segment of Americans at particular risk of social isolation, loneliness and their negative impacts are select populations who live in rural areas.
“There is an urgent need to take action and improve mental health in rural America,” said Jeff Winton, dairy farmer and founder and chairman of Rural Minds, a nonprofit mental health advocacy organization that partnered with Pfizer to raise awareness about the physical and mental risks of social isolation. “Challenges to mental health can be inherent in a rural lifestyle, including a belief in self-reliance as a virtue, fear of judgment and difficulty getting an appointment with a limited number of mental health professionals, among others.”
Many Americans are increasingly spending more time alone according to the American Time Use Survey. They are increasingly more likely to take meetings, shop, eat and enjoy entertainment at home, making it easier for them to stay within their own four walls and avoid social interactions.
Authentic human connection is a basic but often unacknowledged necessity for health, “as essential to survival as food, water and shelter,” according to the U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory on the Health Effects of Social Connection and Community.
Understanding Social Isolation
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about one-third of U.S. adults reported feeling lonely and about one-fourth said they don’t have social and emotional support (the basis of social isolation).
The concepts of social isolation and loneliness can go hand-in-hand, but the two are actually quite different.
Social isolation is defined by an absence of relationships or contact with others. Someone experiencing loneliness may or may not have social connections, but lacks feelings of closeness, support or belonging. Despite the distinction, both can have a negative impact on a person’s mental and even physical health.
Several factors can influence a person’s risk for social isolation and loneliness.
“Social connection is a dynamic that changes over time,” said Nikki Shaffer, senior director, occupational health and wellness, Pfizer. “Transient feelings of loneliness or solitude may be beneficial because they can serve as motivation to reconnect. However, chronic loneliness (even if someone is not isolated) and isolation (even if someone is not lonely) can represent significant health concerns.”

Isolation in Rural America
Compared to people who live in urban areas, many rural Americans experience higher rates of depression and suicide but are less likely to access mental health care services, according to the “Health Disparities in Rural America: Current Challenges and Future Solutions” study published in “Clinical Advisor.” What’s more, CDC data shows suicide rates among people living in rural areas can be 64-68% higherthan those in large urban areas.
Rural areas have 20% fewer primary care providers compared to urban areas, according to a report in JAMA, and the Health Resources and Services Administration reports more than 25 million rural Americans, more than half of rural residents, live in mental health professional shortage areas.
Among rural counties, 65% lack a psychiatrist. Nearly 30% of rural Americans don’t have internet access in their homes, which complicates the option for telehealth. These figures from Rural Minds exemplify the challenges facing rural America.
“Some people in rural communities still don’t understand or accept that mental illness is a disease,” said Winton, who grew up on a rural farm. “Rather, a mental illness can often be viewed as a personal weakness or character flaw. A lot of the stigma around mental illness results in unwarranted shame, which adds to the burden for someone already suffering from mental illness.”
Health Impacts of Social Isolation
Loneliness is far more than just a bad feeling; it harms both individual and societal health. In fact, loneliness and social isolation can increase the risk for premature death by 26% and 29%, respectively.
Lacking social connection can increase the risk for premature death as much as smoking up to 15 cigarettes a day or drinking six alcoholic drinks daily.
In addition, poor or insufficient social connection is associated with increased risk of disease, including a 29% increased risk of heart disease and a 32% increased risk of stroke.
Social isolation is also associated with increased risk for anxiety, depression and dementia. Additionally, a lack of social connection may increase susceptibility to viruses and respiratory illness.
Learn more about the impact of social isolation, especially on residents of rural areas, and the steps you can take to reduce isolation and loneliness by visiting ruralminds.org.
Boost Your Social Connections
Take a proactive approach to combatting social isolation and loneliness with these everyday actions that can promote stronger social ties.
- Invest time in nurturing your relationships through consistent, frequent and high-quality engagement with others. Take time each day to reach out to a friend or family member.
- Minimize distractions during conversation to increase the quality of the time you spend with others. For instance, don’t check your phone during meals with friends, important conversations and family time.
- Seek out opportunities to serve and support others, either by helping your family, co-workers, friends or people in your community or by participating in community service.
- Be responsive, supportive and practice gratitude. As you practice these behaviors, others are more likely to reciprocate, strengthening social bonds, improving relationship satisfaction and building social capital.
- Participate in social and community groups such as religious, hobby, fitness, professional and community service organizations to help foster a sense of belonging, meaning and purpose.
- Seek help during times of struggle with loneliness or isolation by reaching out to a family member, friend, counselor, health care provider or the 988 crisis line.
Photos courtesy of Shutterstock
SOURCE:
Rural Minds and Pfizer
Live Better
Homeowners handbook: Navigating new HVAC refrigerants

(Family Features) Homeowners may not realize it, but one compound impacts their lives nearly every day: refrigerant. Capable of transforming from liquid to gas and back again, it absorbs and transfers heat as a key part of air conditioning and heat pump systems that keep you comfortable no matter the weather.
As part of your air conditioner or heat pump system, it helps transfer heat and humidity out of your home for cooling or draws heat from outdoor air and brings it inside for heating. However, while concerns about climate change heat up, government leaders are enacting policies that enforce greater control over the anticipated global warming potential (GWP) of refrigerants.
In fact, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is limiting the GWP of refrigerants in equipment starting in 2025. At the same time, the EPA is implementing a phasedown on the supply of existing, higher GWP refrigerants.
The changes include a phasedown of high-GWP refrigerants commonly used in home air conditioning and refrigeration, introduction of alternative refrigerants with lower GWP that maintain efficiency and requiring manufacturers to comply with new standards for energy efficiency and environmental impact.
Despite these policy updates, you may not necessarily need a new air conditioner or heat pump. Here’s what homeowners need to know, courtesy of the experts at Carrier, a world leader in high-technology heating, air conditioning and refrigeration solutions:
Environmental Awareness and the Impact on Existing Home Systems
Transitioning away from high-GWP refrigerants contributes positively toward reducing your carbon footprint. These anticipated changes aim not only at reducing environmental impact but also at promoting technological advancements in heating and cooling solutions that benefit both consumers and the planet over time. If you have an existing system using older refrigerants like R-22 or R-410A, it can still be serviced; however, it’s possible repair costs may increase due to reduced availability.
Maintenance and Servicing
Regular maintenance becomes more crucial as systems age. Ensure your HVAC technician is knowledgeable about the new requirements and safely handling different types of refrigerants.
Considerations for New Purchases
When purchasing a new air conditioner or heat pump, be sure to check for energy efficiency ratings that align with the updated regulations and look for models using low-GWP refrigerants. For example, Puron Advance from Carrier will replace existing refrigerants in all its residential ducted and ductless and light commercial products. This innovative refrigerant, also known as R-454B, not only meets the EPA’s anticipated GWP limits for refrigerants but exceeds the new requirements with a GWP of 466, a 75% reduction compared to R-410A.
Incentives and Rebates
If you’re shopping for a new air conditioner or heat pump, keep an eye out for government incentives or rebates aimed at encouraging homeowners to upgrade their systems in compliance with new standards.
Consult Professionals
Owning a home is a lot of work on its own, and EPA regulations on your cooling and heating systems may be the furthest thing from your mind. If you believe you’re due for service or a new system, engage HVAC professionals – like the trusted experts at Carrier – who are up to date on regulatory changes. Always check local regulations for specific details applicable in your area since policies can vary by region beyond federal guidelines.
To find more information on the changes or connect with an HVAC professional, visit Carrier.com/Residential.
SOURCE:
Carrier
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years ago2 hurt, 1 jailed after shooting incident north of Nocona
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSuspect indicted, jailed in Tia Hutson murder
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSO investigating possible murder/suicide
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoWreck takes the life of BHS teen, 16
-
 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoMurder unsolved – 1 year later Tia Hutson’s family angry, frustrated with no arrest
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSheriff’s office called out to infant’s death
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoBowie Police face three-hour standoff after possible domestic fight
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoDriver stopped by a man running into the street, robbed at knifepoint






