HEALTHY LIVING
6 steps to get better sleep, improve heart health

(Family Features) There’s more to maintaining a healthy heart than just eating right and exercising regularly. While these practices play an important role in both cardiovascular and overall health and well-being, getting a good night’s sleep is also key.
“Getting a good night’s sleep every night is vital to cardiovascular health,” said Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, M.D., Sc.M., FAHA, past volunteer president of the American Heart Association and chair of the department of preventive medicine, the Eileen M. Foell Professor of Heart Research and professor of preventive medicine, medicine and pediatrics at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine. “Adults should aim for an average of 7-9 hours, and babies and kids need more depending on their age.”
However, more than 1 in 3 adults in the United States are not getting the recommended 7-9 hours of sleep per night, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In addition to increasing risk for cardiovascular conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, heart attack and stroke, lack of sleep may also put people at risk of depression, cognitive decline, diabetes and obesity.
While high blood pressure – a known risk factor of cardiovascular disease, the No. 1 cause of death worldwide – can run in families, it is more common in non-Hispanic Black adults (56%) than in non-Hispanic white adults (48%), non-Hispanic Asian adults (46%) or Hispanic adults (39%). Healthy lifestyle behaviors, including sleep, can help prevent the condition.
“We know that people who get adequate sleep manage other health factors better as well, such as weight, blood sugar and blood pressure,” Lloyd-Jones said. “The American Heart Association added sleep to the list of factors that support optimal cardiovascular health. We call these Life’s Essential 8, and they include: eating a healthy diet, not smoking or vaping, being physically active and getting adequate sleep along with controlling your blood pressure and maintaining healthy levels of cholesterol and lipids, healthy blood sugar levels and a healthy weight.”
What’s more, falling asleep at different times or sleeping an inconsistent number of hours each night, even variations of more than two hours a night within the same week, may also increase the risk of atherosclerosis, which is a cardiovascular condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, in those age 45 and older, according to research published in the “Journal of the American Heart Association.”
“Maintaining regular sleep schedules and decreasing variability in sleep is an easily adjustable lifestyle behavior that can not only help improve sleep, but also help reduce cardiovascular risk for aging adults,” said study lead author Kelsie Full, Ph.D., M.P.H., an assistant professor of medicine in the division of epidemiology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center.
Education about healthy heart habits from the American Heart Association is nationally supported by Elevance Health Foundation. Some practices to improve sleep health and impact heart health include:
Observe Current Sleep Habits
Keeping a sleep diary to help track your sleep patterns and habits can make it easier to identify factors that may be helping – or hurting – your sleep quality. Monitor what time you go to bed, what time you wake up in the morning, how many times you woke up during the night, how you felt when you woke up and any variables, such as changes to your routine or sleeping arrangements. Having documentation over the course of several weeks can help you identify necessary changes.
Avoid Food and Beverage Close to Bedtime
It can be more difficult to fall asleep if you’re still digesting dinner. To help reduce sleep disruptions caused by food, avoid late dinners and minimize fatty and spicy foods. Similarly, keep an eye on caffeine intake and avoid it later in the day when it can be a barrier to falling asleep.
Exercise Regularly
Physical activity during the day can have a noticeable impact on overall health and wellness but can also make it easier to sleep at night as it can initiate changes in energy use and body temperature. However, exercising too close to bedtime may hinder your body’s ability to settle; aim to have your workout complete at least four hours before you plan to head to bed.
Establish a Bedtime Routine
Getting a good night’s rest often requires getting into a routine. Start by setting an alarm to indicate it’s time to start winding down. Rather than heading straight to bed, take time to create a to-do list for the following day and knock out a few small chores. Then consider implementing a calming activity like meditating, journaling or reading (not on a tablet or smartphone) before drifting off to sleep. Also set an alarm to wake each morning, even on weekends, and avoid hitting the snooze button to keep your biological rhythms synced.
Create a Comfortable Sleep Space
The ideal space for sleeping is dark, quiet and a comfortable temperature, typically around 65 F depending on the individual. Use room-darkening curtains or a sleep mask to block light and ear plugs, a fan or a white noise machine to help drown out distracting noises. Remember, using your bed only for sleep and sex can help establish a strong mental association between your bed and sleep.
Avoid Tech Before Bed
The bright light of televisions, computers and smartphones can mess with your Circadian rhythm and keep you alert when you should be winding down. Try logging off electronic devices at least one hour before bedtime and use the “do not disturb” function to avoid waking up to your phone throughout the night. Better yet, charge devices away from your bed or in another room entirely.
Find more tips to take control of your blood pressure and create healthy sleep habits at Heart.org.
Photo courtesy of Getty Images
SOURCE:
American Heart Association
HEALTHY LIVING
How to conduct a skin care self-exam
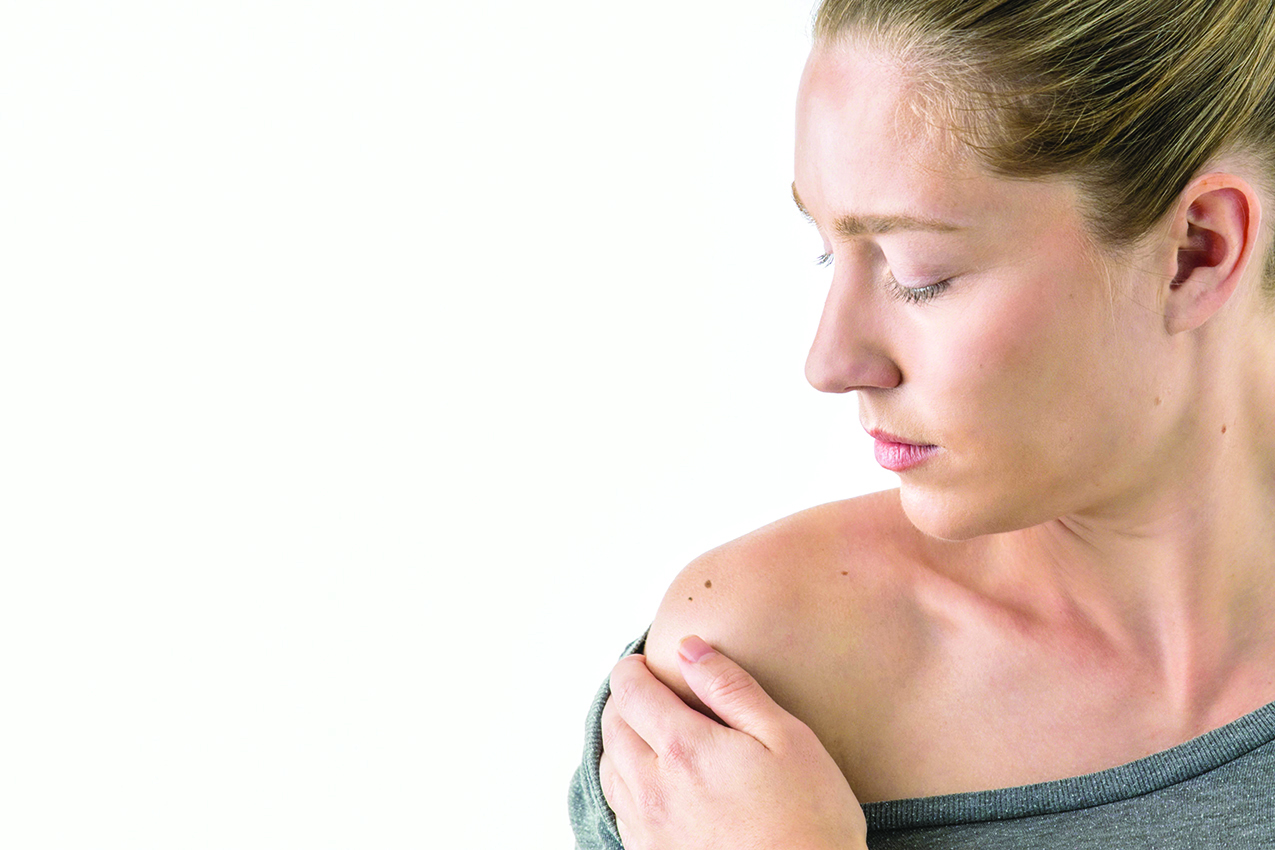
Time spent soaking up the summer sun is one of the things that makes the season so appealing. Warm outdoor air has a calming effect that can make anyone feel more relaxed and comfortable.
As good as warm summer sun can feel, overexposure to the sun can be dangerous. The World Cancer Research Fund reports there were more than 330,000 new cases of skin cancer diagnosed across the globe in 2022. A significant percentage of skin cancer cases can be prevented, and prevention is a multifaceted process that includes skin care self-examinations. Self-exams do not take up much time, and individuals can speak with their physicians about how frequently they should check their skin for signs of skin cancer. The U.S. National Library of Medicine offers the following instructions for how to conduct a skin self-exam.
Choose the right time to examine your skin. The USNLM recommends conducting a skin exam after bathing. Women who routinely conduct breast self-exams can check their skin at this time as well.
Use a full-length mirror. ItÕs not always easy to examine skin throughout the body. But signs of skin problems can occur anywhere on the body, including areas that might be hard to see without help. If possible, conduct a self-exam of the skin in front of full-length mirror in a brightly lit room.
Identify what youÕre looking for. The USNLM notes you should be looking for any new skin markings. This includes bumps, moles, blemishes, and changes in skin color.
Pay close attention to preexisting moles. A potential sign of skin cancer includes moles that change over time. Examine preexisting moles to see if they have changed in size, texture, color, and shape.
Look for unusual moles. The USNLM characterizes certain moles as Òugly duckling moles.Ó These unique moles look and feel different from nearby moles and may be indicative of skin cancer. Speak with a dermatologist if a self-exam uncovers the presence of moles with uneven edges or differences in colors or asymmetric shapes. Moles that look different from one side to the other also should be brought to the attention of a dermatologist. Moles that do not stop bleeding or will not heal also merit examination by a skin care professional.
When the time comes to conduct the exam, the USNLM recommends following these steps:
- Look closely at your entire body, both front and back, in the mirror.
- Check under your arms and on both sides of each arm. Be sure to examine the backs of your upper arms, which can be hard to see.
- Bend your arms at the elbow, and examine both sides of your forearm.
- Examine the tops and palms of your hands.
- Examine the front and back of both legs.
- Examine your buttocks and between your buttocks.
- Examine your genital area.
- Examine your face, neck, the back of your neck, and scalp. Use both a hand mirror and full-length mirror, along with a comb, to see areas of your scalp.
- Examine your feet, including the soles and the spaces between your toes.
- Ask a person you trust to help examine hard-to-see areas.
Skin cancer poses a formidable threat, but many cases of the disease are preventable. Routine skin self-exams are a vital component of skin cancer prevention. TF256909
HEALTHY LIVING
What does 100% grass-fed organic dairy bring to your table

(Family Features) It’s no secret that many grocery store dairy sections are filled with more options today. One choice continuing to gain favor with consumers is 100% grass-fed organic dairy. Nutrition, environmental awareness and animal care are some of the leading reasons consumers choose grass-fed dairy products.
Globally, the 100% grass-fed dairy market is projected to continue growing and some market experts predict annual growth rates as high as 22%. If you’re curious about 100% grass-fed organic dairy, consider these benefits from Maple Hill, America’s original 100% grass-fed organic dairy producer. The pioneer of 100% grass-fed organic dairy took its commitment a step further by celebrating and declaring National 100% Grass-Fed Organic Dairy Day on April 15, which recognizes the positive impact it has on consumers, cows, farmers and the environment.
1. Honoring the Farmers
Unlike large-scale corporate dairy farms, most organic farms are small, family-owned operations dedicated to traditional, sustainable farming. Small dairy farms have been disappearing, but 100% grass-fed organic dairy creates a sustainable, viable path forward for farmers who work in harmony with nature.
This more natural approach to dairy is a “craft” process favoring small family farmers who are willing to dedicate the extra focus and patience to a better product and process. These family farms are passed on to future generations to grow the “better for you, better for the planet” approach.
2. Commitment to Good Health
Most consumers don’t know the difference between traditional organic and 100% grass-fed organic dairy. One key distinction is the products’ nutritional composition; 100% grass-fed organic dairy provides a 50% healthier ratio of omega 3:6 and 40% higher levels of CLA fatty acids, which may support heart health and provide other health benefits.
What’s more, Maple Hill’s products made with 100% grass-fed organic dairy are GMO free, hormone free and antibiotic free with no additives or fillers. The line of high-quality, rich-flavored products let you experience the organic difference from traditional dairy for a nutrient-dense solution that tastes as nature intended.
3. Happy, Healthy Cows
Cows on a 100% grass-fed diet can live up to three times as long as grain-fed cows and are never subjected to unnatural diets, hormones or antibiotics. More time in pastures filled with lush grass means cows have the freedom to roam, ruminate and graze on diverse, nutrient-rich grasses.
The result is happier, healthier cows, which in turn results in a richer, better-tasting and more nutrient-dense milk.
4. Sustainability and the Environment
Producing milk without grain or corn requires farmers to focus on regenerating soil and the soil life that supports everything else on the farm. In fact, the healthier the soil, the healthier the feed, so farmers have a natural incentive to be as regenerative as possible. Regenerative grazing practices are a powerful and positive tool to improve land and the web of life on farms by actively restoring soil health, promoting biodiversity and reducing the environmental impact compared to conventional dairy.
Well-managed grazing helps pull carbon from the atmosphere into the soil, fighting climate change in the process. In addition, healthier soil retains more water, reducing runoff and protecting water sources from agricultural pollution.
5. Strengthening the 100% Grass-Fed Organic Market
Consumers are increasingly aware of the choices they have in dairy products and how 100% grass-fed organic supports their health, farmers, animals and the planet. Some ways to support this category’s continued growth include choosing certified 100% grass-fed organic dairy, advocating for regenerative farming and helping shape a more sustainable food system.
Learn more about 100% grass-fed organic dairy products at maplehill.com.
SOURCE:
HEALTHY LIVING
Promote health with these daily habits

Health should be a priority, but too often life gets in the way and individuals take a reactive, rather than proactive, approach to their personal well-being. But living healthier need not be so difficult. In fact, research suggests that small, positive changes in how a person lives each day creates a healthier person over time.
A Hologic-Gallup survey on the state of women’s health conducted in April 2024 found 63 percent of respondents said it was hard for them to make health a priority. They cited feeling overwhelmed, needing to care for others before themselves, emotional/mental health, and work as the top barriers to focusing on health. But it’s important that both women and men recognize that small changes can add up to big results. These healthy habits can help individuals start living healthier lifestyles.
· Get some exercise. Regular physical activity is one of the most important things a person can do fo his or her health. Exercise helps manage weight, reduces the risk of disease, strengthens bones and muscles, and improves brain health. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says adults should aim for at least 150 minutes (30 minutes a day for five days) of moderate-intensity aerobic activity a week. A great place to begin is with a daily walk, which is a simple and effective habit that does not require a lot of time and no equipment except a good pair of athletic shoes.
· Wear sunscreen every day. After washing your face each morning, apply a facial moisturizer with an SPF of at least 30, or blend equal parts of sunscreen and regular moisturizer, suggests Harvard Health. Use it on the face, neck, ears, and any thinning hair spots on the scalp. Skin cancer is the most common type of the disease worldwide, and wearing sunscreen can help many people avoid it.
· Spend time outdoors. It takes just a few minutes in the sun to raise vitamin D levels. Vitamin D is necessary for bone and heart health and helps to boost mood, says WebMD. Various studies indicate spending time in green spaces promotes calm and increases happiness.
· Plan your meals. Meal planning is not just a way to manage food budgets. It’s also a great method to being more mindful of food choices and avoiding impulse buys or meals that may not be as healthy as they can be. Adding more plant-based foods to a diet is a good start. Such foods can reduce the risk of chronic conditions like high cholesterol and hypertension.
· Stay hydrated. Hydration supports good digestion, increases energy and may improve brain performance, states Harvard Health. Drink a glass of water each day upon waking up and with every meal. Older adults often do not feel thirst like they did when they were younger, so it is especially important for seniors to stay hydrated.
Healthy habits are more easily adopted when people begin small and make a daily commitment to their overall health.
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years ago2 hurt, 1 jailed after shooting incident north of Nocona
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSuspect indicted, jailed in Tia Hutson murder
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSO investigating possible murder/suicide
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoWreck takes the life of BHS teen, 16
-
 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoMurder unsolved – 1 year later Tia Hutson’s family angry, frustrated with no arrest
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSheriff’s office called out to infant’s death
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoBowie Police face three-hour standoff after possible domestic fight
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoDriver stopped by a man running into the street, robbed at knifepoint






