HEALTHY LIVING
It’s time to rethink heart health


(Family Features) On average, someone in the United States dies from cardiovascular disease (CVD) every 36 seconds, approximately 2,380 deaths each day, according to the American Heart Association. Each day, 405 deaths occur in the U.S. as the result of strokes, an average of one death every 3:33. More people die annually from CVD than from any other cause including cancer, COPD, diabetes, lung infections and the flu, according to the American Heart Association (AHA) 2021 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics.
Consider these steps to #RethinkCVRisk to change the course of the disease and your life.
Understand Your Risk
COVID-19 has shown that those with underlying CVD face an especially high risk of serious COVID-19-related illness or even death, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Regardless of whether you’ve received your COVID-19 vaccination, now is a good time to discuss your risk for heart disease with your doctor.
How Cardiovascular Disease Develops
Risk factors for CVD include high cholesterol, high triglycerides, diabetes and high blood pressure. Other factors that contribute to risk are family history, prior cardiovascular (CV) events, smoking, being overweight or obese and unhealthy diet and exercise habits. Over time, these risk factors can lead to injury of the blood vessel lining, causing inflammation, which can then trigger plaque growth. Plaque grows at different rates and in different arteries in the body for everyone and is often a slow, gradual process without symptoms.
As plaque buildup continues, the risk of suffering a CV event – such as heart attack or stroke – increases. If plaque ruptures, the body will try to repair the injury, potentially causing a blockage to form, and when an artery becomes fully blocked, blood flow is restricted. Blocked blood flow to the heart causes a heart attack while blocked blood flow to the brain causes a stroke.

Managing Risk Factors
The most effective way to prevent CVD is to understand and address risk factors. Triglycerides play an important role in heart health. Triglycerides store unused calories to give your body energy and are the most common type of fat in the body. They come from foods you eat such as butter, oils and other fats, as well as carbohydrates, sugars and alcohol. Your diet, lack of exercise, medical conditions, certain drugs and genetics can all cause high triglycerides.
In the past, medicines used to lower triglycerides, like fenofibrates and niacin, were commonly prescribed to help manage CV risk along with statins. However, clinical studies failed to show benefits and both the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and American Diabetes Association discourage combining niacin and fenofibrates with statins.
Some turn to dietary supplement fish oil to help manage CV risk. However, supplements contain only 30% of the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) with the majority of the product consisting of non-omega-3 ingredients, including saturated fats. Some data suggests certain ingredients in dietary supplement fish oils, such as DHA and saturated fats, may raise bad cholesterol.
While high triglycerides are an indicator of CV risk, lowering them won’t necessarily reduce your risk. However, addressing the underlying causes of high triglycerides can help, according to the AHA.
Treatment Options
With ongoing research, new standards-of-care are emerging. High cholesterol is a key CV risk factor with statins currently the first-line therapy for lowering cholesterol. Statins, diet and exercise can lower your CV risk by about 25-35%, but, for many people, controlled cholesterol doesn’t eliminate CV risk. This residual risk, or “persistent CV risk,” puts millions of patients at risk and has been the focus of therapeutic development for many years.
Talk with your doctor about FDA-approved options that can help further reduce your heart risk if you already take statins.
Truths and Falsehoods About Heart Disease Risk
1. Statins reduce your chance of experiencing a CV event by up to 90%.
False. Statins, diet and exercise can lower your risk by about 25-35%, but for many patients, controlled cholesterol doesn’t eliminate CV risk. This residual risk, or “persistent CV risk,” puts millions of patients at risk and has been the focus of therapeutic development for many years.
2. Managing high triglycerides along with taking statins is enough to reduce your risk.
False. High triglycerides are a CV risk factor but lowering them won’t necessarily reduce your risk. For example, earlier generation medicines prescribed to lower triglycerides, like fenofibrates and niacin, failed to show clinical benefit when used with statins to reduce CV risk. In fact, the FDA withdrew approval for fenofibrates and niacin in combination with statins because they add potential risk with no proven benefit to heart health.
3. Fish oil supplements are a proven way to get protection from a CV event.
False. Fish oil supplements are not FDA-approved medicines intended to treat or prevent a medical condition. Despite multiple clinical studies, these products have not been proven, to reduce CV risk on top of current medical therapies including statins.
4. Having a first CV event, such as a heart attack or stroke, puts you at greater risk to suffer another.
True. Having a CV event makes you more likely to suffer another. That’s why it’s important to protect against a first CV event or future events. To closely monitor your heart health, stay in close contact with your doctor and reduce your risk by keeping up with your medications, exercising and sticking to a healthy diet.
For more information about CVD and what you can do, look for #RethinkCVRisk on social media or visit truetoyourheart.com.
Photos courtesy of Getty Images
SOURCE:
Amarin Pharma, Inc.
HEALTHY LIVING
What does 100% grass-fed organic dairy bring to your table

(Family Features) It’s no secret that many grocery store dairy sections are filled with more options today. One choice continuing to gain favor with consumers is 100% grass-fed organic dairy. Nutrition, environmental awareness and animal care are some of the leading reasons consumers choose grass-fed dairy products.
Globally, the 100% grass-fed dairy market is projected to continue growing and some market experts predict annual growth rates as high as 22%. If you’re curious about 100% grass-fed organic dairy, consider these benefits from Maple Hill, America’s original 100% grass-fed organic dairy producer. The pioneer of 100% grass-fed organic dairy took its commitment a step further by celebrating and declaring National 100% Grass-Fed Organic Dairy Day on April 15, which recognizes the positive impact it has on consumers, cows, farmers and the environment.
1. Honoring the Farmers
Unlike large-scale corporate dairy farms, most organic farms are small, family-owned operations dedicated to traditional, sustainable farming. Small dairy farms have been disappearing, but 100% grass-fed organic dairy creates a sustainable, viable path forward for farmers who work in harmony with nature.
This more natural approach to dairy is a “craft” process favoring small family farmers who are willing to dedicate the extra focus and patience to a better product and process. These family farms are passed on to future generations to grow the “better for you, better for the planet” approach.
2. Commitment to Good Health
Most consumers don’t know the difference between traditional organic and 100% grass-fed organic dairy. One key distinction is the products’ nutritional composition; 100% grass-fed organic dairy provides a 50% healthier ratio of omega 3:6 and 40% higher levels of CLA fatty acids, which may support heart health and provide other health benefits.
What’s more, Maple Hill’s products made with 100% grass-fed organic dairy are GMO free, hormone free and antibiotic free with no additives or fillers. The line of high-quality, rich-flavored products let you experience the organic difference from traditional dairy for a nutrient-dense solution that tastes as nature intended.
3. Happy, Healthy Cows
Cows on a 100% grass-fed diet can live up to three times as long as grain-fed cows and are never subjected to unnatural diets, hormones or antibiotics. More time in pastures filled with lush grass means cows have the freedom to roam, ruminate and graze on diverse, nutrient-rich grasses.
The result is happier, healthier cows, which in turn results in a richer, better-tasting and more nutrient-dense milk.
4. Sustainability and the Environment
Producing milk without grain or corn requires farmers to focus on regenerating soil and the soil life that supports everything else on the farm. In fact, the healthier the soil, the healthier the feed, so farmers have a natural incentive to be as regenerative as possible. Regenerative grazing practices are a powerful and positive tool to improve land and the web of life on farms by actively restoring soil health, promoting biodiversity and reducing the environmental impact compared to conventional dairy.
Well-managed grazing helps pull carbon from the atmosphere into the soil, fighting climate change in the process. In addition, healthier soil retains more water, reducing runoff and protecting water sources from agricultural pollution.
5. Strengthening the 100% Grass-Fed Organic Market
Consumers are increasingly aware of the choices they have in dairy products and how 100% grass-fed organic supports their health, farmers, animals and the planet. Some ways to support this category’s continued growth include choosing certified 100% grass-fed organic dairy, advocating for regenerative farming and helping shape a more sustainable food system.
Learn more about 100% grass-fed organic dairy products at maplehill.com.
SOURCE:
HEALTHY LIVING
Promote health with these daily habits

Health should be a priority, but too often life gets in the way and individuals take a reactive, rather than proactive, approach to their personal well-being. But living healthier need not be so difficult. In fact, research suggests that small, positive changes in how a person lives each day creates a healthier person over time.
A Hologic-Gallup survey on the state of women’s health conducted in April 2024 found 63 percent of respondents said it was hard for them to make health a priority. They cited feeling overwhelmed, needing to care for others before themselves, emotional/mental health, and work as the top barriers to focusing on health. But it’s important that both women and men recognize that small changes can add up to big results. These healthy habits can help individuals start living healthier lifestyles.
· Get some exercise. Regular physical activity is one of the most important things a person can do fo his or her health. Exercise helps manage weight, reduces the risk of disease, strengthens bones and muscles, and improves brain health. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says adults should aim for at least 150 minutes (30 minutes a day for five days) of moderate-intensity aerobic activity a week. A great place to begin is with a daily walk, which is a simple and effective habit that does not require a lot of time and no equipment except a good pair of athletic shoes.
· Wear sunscreen every day. After washing your face each morning, apply a facial moisturizer with an SPF of at least 30, or blend equal parts of sunscreen and regular moisturizer, suggests Harvard Health. Use it on the face, neck, ears, and any thinning hair spots on the scalp. Skin cancer is the most common type of the disease worldwide, and wearing sunscreen can help many people avoid it.
· Spend time outdoors. It takes just a few minutes in the sun to raise vitamin D levels. Vitamin D is necessary for bone and heart health and helps to boost mood, says WebMD. Various studies indicate spending time in green spaces promotes calm and increases happiness.
· Plan your meals. Meal planning is not just a way to manage food budgets. It’s also a great method to being more mindful of food choices and avoiding impulse buys or meals that may not be as healthy as they can be. Adding more plant-based foods to a diet is a good start. Such foods can reduce the risk of chronic conditions like high cholesterol and hypertension.
· Stay hydrated. Hydration supports good digestion, increases energy and may improve brain performance, states Harvard Health. Drink a glass of water each day upon waking up and with every meal. Older adults often do not feel thirst like they did when they were younger, so it is especially important for seniors to stay hydrated.
Healthy habits are more easily adopted when people begin small and make a daily commitment to their overall health.
HEALTHY LIVING
Make a smart home investment with an all climate heat pump

(Family Features) If your home uses a conventional heating and cooling system, you may wonder if there’s a better way to manage indoor comfort. Between rising energy costs and concerns about the efficiency of conventional systems, many homeowners are exploring alternatives. One popular solution is an all-climate heat pump.
All-climate heat pumps are the next generation of heat pump technology built for peak performance, regardless of the outdoor temperature. From the personalized comfort all-climate heat pumps deliver to the energy savings realized, it’s no wonder more homeowners are considering going all-in on all-climate.
If you’re considering replacing your current HVAC system, read on for some of the benefits of all-climate heat pumps.
Personalized Comfort
Ductless, multi-zone, all-climate heat pump systems are designed to deliver personalized, room-to-room temperature control tailored to your preferences. Unlike traditional ducted unitary systems, which typically operate on an all-or-nothing basis, ductless multi-zone solutions provide individualized climate settings for each space. Whether you prefer a warmer living room or a cooler bedroom, the flexibility to adjust each zone offers unparalleled convenience and energy efficiency.
Efficiency
According to a survey of U.S. homeowners commissioned by Mitsubishi Electric Trane HVAC US (METUS), 93% of homeowners surveyed with conventional HVAC systems reported concerns about utility bills. Seventy-five percent of those surveyed also consider energy efficiency always or often when considering home improvements.
Conventional heating and cooling systems run at full capacity to reach set point and then shut off. The start-stop action ultimately wastes energy. With variable-capacity capabilities and inverter-driven technology, all-climate heat pumps can adjust and maintain temperatures, lessening your home’s overall energy demand and driving down cost.
Cost Savings
The cost savings provided by efficient energy usage are evident. Additionally, some states offer rebates for new HVAC systems, and many contractors offer financing options, which make the upfront cost of an all-climate heat pump installation more affordable.
Reliability is another cost-saving factor. All-climate heat pumps are purpose-built with durable materials to perform well in all kinds of weather.
“We continue to educate homeowners about the advantages all-climate heat pumps have over conventional HVAC systems,” said Mark Kuntz, Chief Executive Officer, METUS. “As homeowners become more knowledgeable about the numerous benefits, including personalized comfort, energy efficiency and cost savings, we believe they will increasingly install these next-generation systems in their homes.”
Learn more about how you can better manage your home’s indoor comfort with all-climate heat pump technology by visiting mitsubishicomfort.com.
SOURCE:
Mitsubishi Electric
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years ago2 hurt, 1 jailed after shooting incident north of Nocona
-

 NEWS1 year ago
NEWS1 year agoSuspect indicted, jailed in Tia Hutson murder
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSO investigating possible murder/suicide
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoWreck takes the life of BHS teen, 16
-
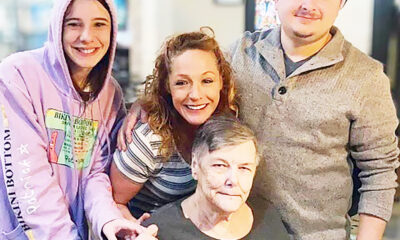
 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoMurder unsolved – 1 year later Tia Hutson’s family angry, frustrated with no arrest
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoSheriff’s office called out to infant’s death
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoBowie Police face three-hour standoff after possible domestic fight
-

 NEWS2 years ago
NEWS2 years agoDriver stopped by a man running into the street, robbed at knifepoint







